Fig 2.
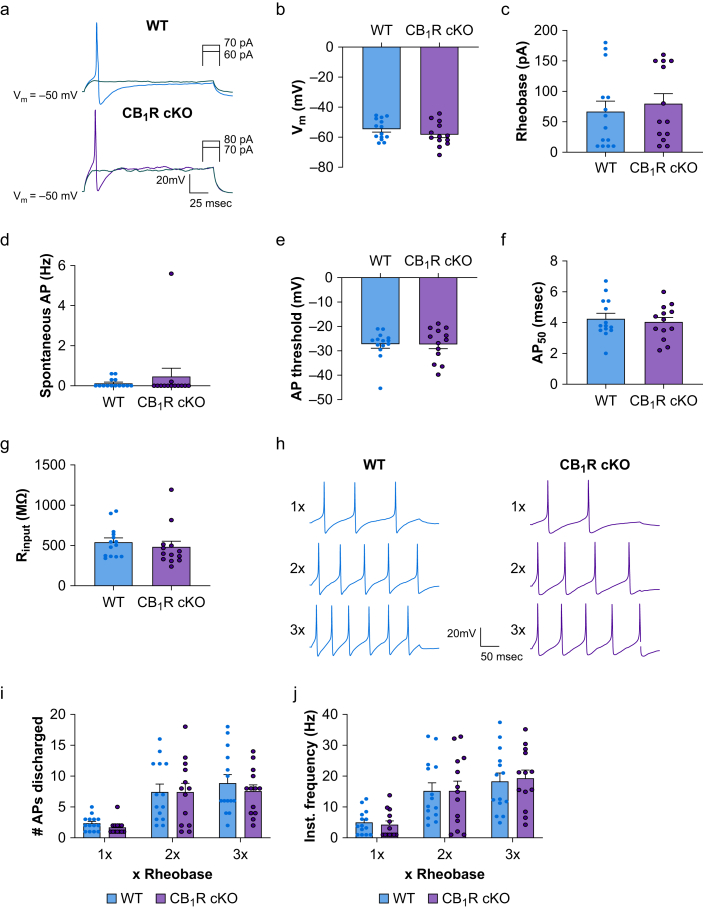
The intrinsic membrane properties of small-diameter dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurones are not affected by CB1R conditional knockout. (a) Representative traces of rheobase levels of small-diameter DRG neurones from wild-type (WT) and CB1R cKO mice under current-clamp conditions. The electrophysiological parameters shown in panels b–g did not differ significantly between the WT and CB1R cKO groups (n=13–14 neurones/group, four mice/sex). (b) Resting membrane potentials (P=0.26). (c) Rheobase levels (P=0.62). (d) Rate of spontaneous action potential (AP) discharge (P=0.76). (e) AP threshold (P=0.97). (f) AP half-width (AP50; P=0.61). (G) Input resistance (Rinput; P=0.48). (h) Representative traces of AP trains evoked by current stimulation (1×, 2×, 3× rheobase intensity) of small-diameter neurones from WT and CB1R cKO mice. (i, j) The number of APs generated (1×: P=0.89, 2×: P=0.98, 3×: P=0.78) and the instantaneous frequency (1×: P=0.99, 2×: P=0.99, 3×: P=0.98) of AP trains discharged by DRG neurones did not differ between WT (n=14 neurones) and CB1R cKO mice (n=13 neurones) across stimulation intensities. (b–g): unpaired t-test; (i, j): two-way mixed-model anova. Data are shown as mean (standard error of the mean). CB1R, cannabinoid type-1 receptor; cKO, conditional knockout; anova, analysis of variance.