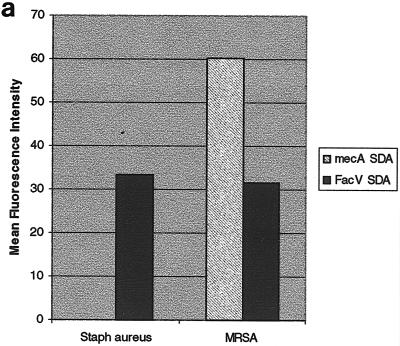
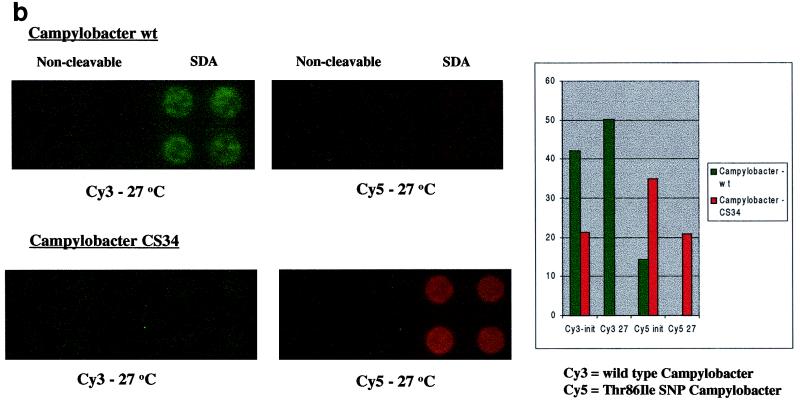
FIG. 3.
(a) Detection of the mecA gene in S. aureus by anchored SDA. Anchored SDA was performed with either methicillin-susceptible (Staph aureus) or methicillin-resistant (MRSA) S. aureus genomic DNA. Factor V-anchored SDA was performed on the same microchip array as a control for the efficiency of the anchored SDA reaction. (b) Discrimination of fluoroquinolone-resistant C. jejuni using anchored SDA. Anchored SDA was performed with 50 ng of C. jejuni genomic DNA samples expressing a wild-type phenotype (wt; top fluorescent image) or containing a fluoroquinolone-resistant point mutation (CS34; bottom fluorescent image). Wild-type reporters (Cy3) and fluoroquinolone-resistant mutant reporters (Cy5) were hybridized to the microchip array, and thermal stringency was applied to discriminate the amplification reaction. Reporter signals remaining after thermal stringency were quantified to determine the genotype of the hybridized genomic DNA sample (graph). init, initial temperature; 27, 27°C.