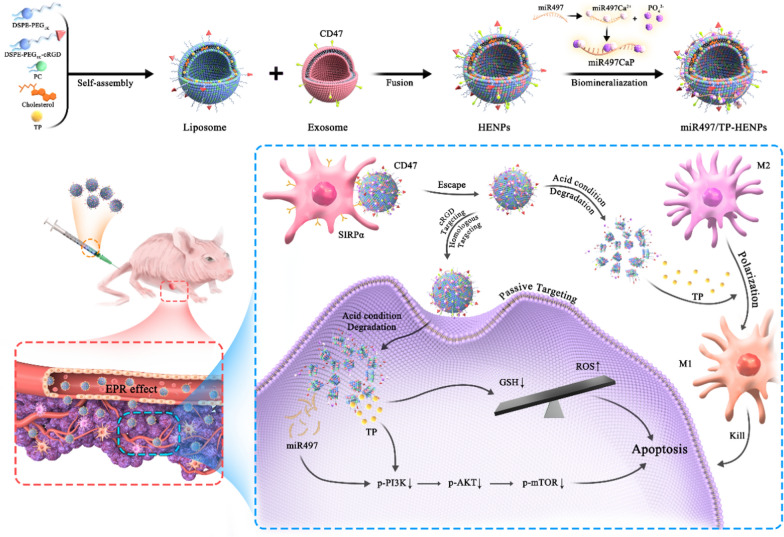
Fig. 1.
Diagram of the formative process and mechanism of action of miR497/TP-HENPs. miR497/TP-HENPs were synthesized by membrane fusion and biomineralization methods. First, liposomes were synthesized by assembly with DSPE-PEG1k-cRGD, phosphatidylcholine (PC), cholesterol and encapsulated TP. Then, liposomes and exosomes were fused by membrane fusion. Finally, CaP adsorbed miR497 on the surface of nanoparticles. The mechanisms by which miR497/TP-HENPs operated in OC cells were as follows: a the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect were generated from the nanoscale size of the nanoplatforms, b the homing targeting of exosomes and cRGD further enhanced the targeting efficiency of nanoparticles, c CD47 on the exosome surface avoided nanoparticle clearance by the MPS system, d miR497 and TP synergistically inhibited the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, e TP stimulated ROS production, and f TP modulated polarization of M2 macrophages into M1 macrophages, synergistically overcoming OC resistance