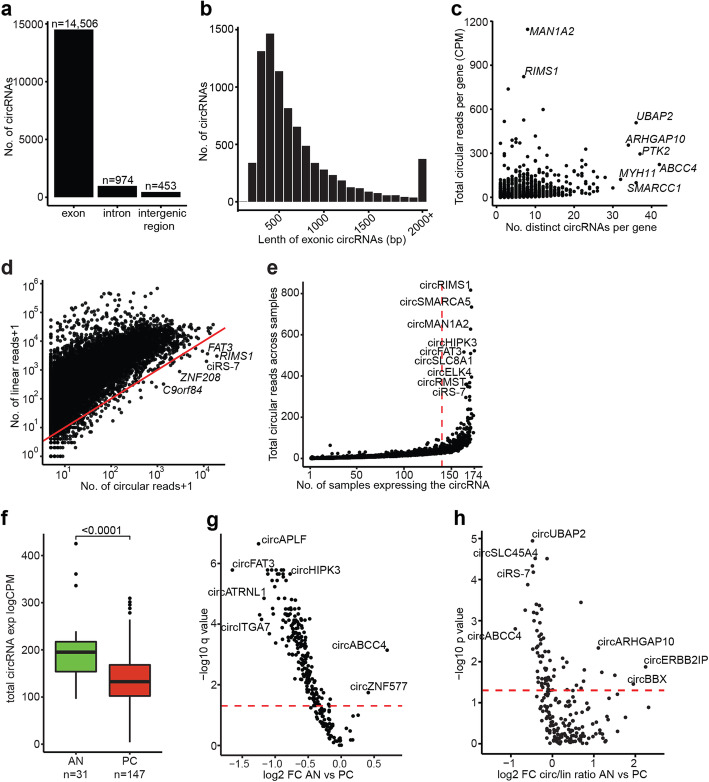
Fig. 2.
Profiling of circRNAs in prostate cancer patients. a Genomic origin of circRNAs. b Estimated exonic length of circRNAs. Bin size = 100 bp. c Number of total circular reads (CPM) per gene versus number of distinct circRNAs per gene. d For each circRNA, the number of circular and corresponding linear reads on a logarithmic scale. Above the red line: Linear > circRNA, below the red line: circRNA > linear. e Total number of circular reads across all patient samples vs. the number of samples expressing each distinct circRNA. The red dotted line marks circRNAs detected in more than 80% of all samples. f Boxplot of total expression (CPM) of abundant circRNA across cancer (LPC and MPC) and AN samples in cohort 1. P value represents Wilcoxon rank-sum test. g–h Volcano plot of (g) abundant circRNAs or (h) circ/lin ratio for abundant circRNAs showing log2 fold change between cancer and AN samples in cohort 1 according to the levels of significance. Horizontal dashed line corresponds to q (g) or p (h) = 0.05. X-axis and Y-axis are plotted on a logarithmic scale (log2 and log10, respectively). CPM = counts per million. FC = fold change