Fig. 3 |. Correction of hemodynamic artifacts with alternating violet and blue illumination.
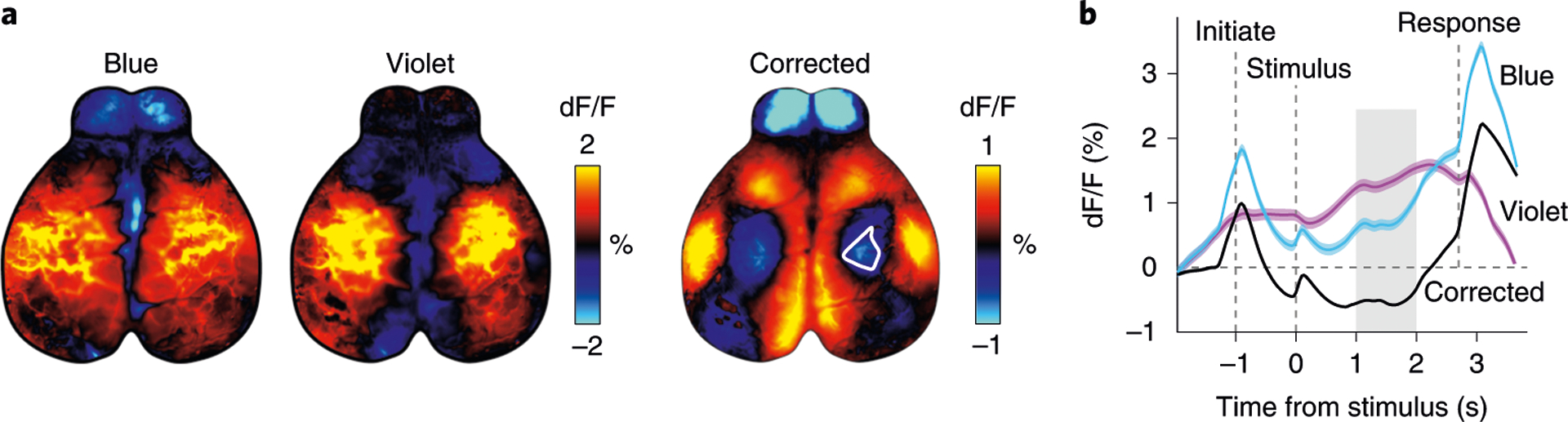
a, Trial-averaged fluorescence with either blue or violet excitation (left) during a behavioral task4 (n = 402 trials). Hemodynamic corrected trial average (right) shows reduced activity in the hind-limb area (white outline). b, Hemodynamic correction recovers the temporal dynamics of neural signals. Traces show averaged fluorescence from the somatosensory hind-limb area (white outline in a), which appears to be above baseline when averaging activity acquired with blue excitation. However, the hemodynamic corrected trace (black) shows that activity is below baseline. Gray shading shows the time from which maps in a were averaged. Dashed lines show the time of different events in the task. Animal experiments followed NIH guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
