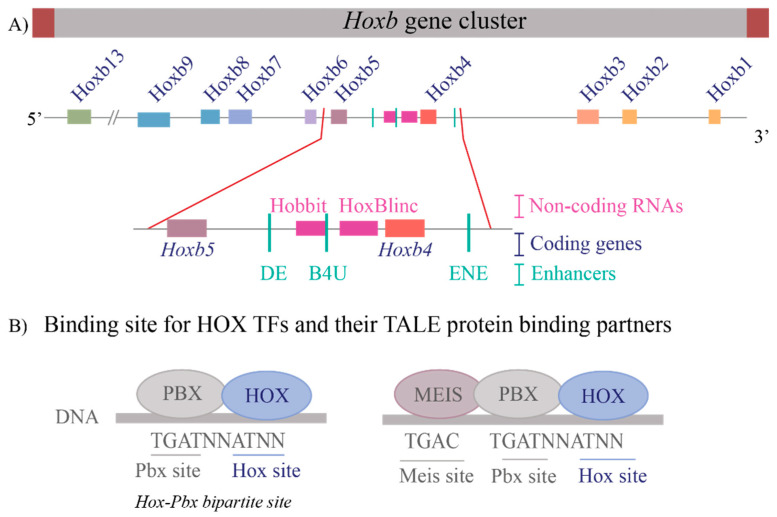
Figure 2.
Transcriptional complexity of the Hoxb gene cluster and binding of HOX Transcription factors to DNA (A) A drawing of the Hoxb gene cluster to illustrate that non-coding RNAs as well as enhancers that contain RAREs (Retinoic Acid Response Elements) are interspersed within the coding Hox genes. The enlargement of the Hoxb4-Hoxb5 region shows the complexity within the region that contains three RAREs, two present upstream of Hoxb4 and one present downstream of Hoxb4 and two non-coding RNAs, Hobbit and HoxBlinc. Brown boxes flank the cluster depict boundary elements, colored squares are different Hox genes, pink boxes are non-coding RNAs, and green lines represent RARE enhancers. (B) Depicts the consensus DNA binding sites for HOX proteins and their binding partners, the TALE proteins PBX and MEIS. HOX proteins can bind on Hox-Pbx bipartite sites, or they can bind on DNA in ternary complexes along with both PBX and MEIS. Blue ovals are HOX proteins, and grey ovals are TALE protein binding partners.