FIG 4.
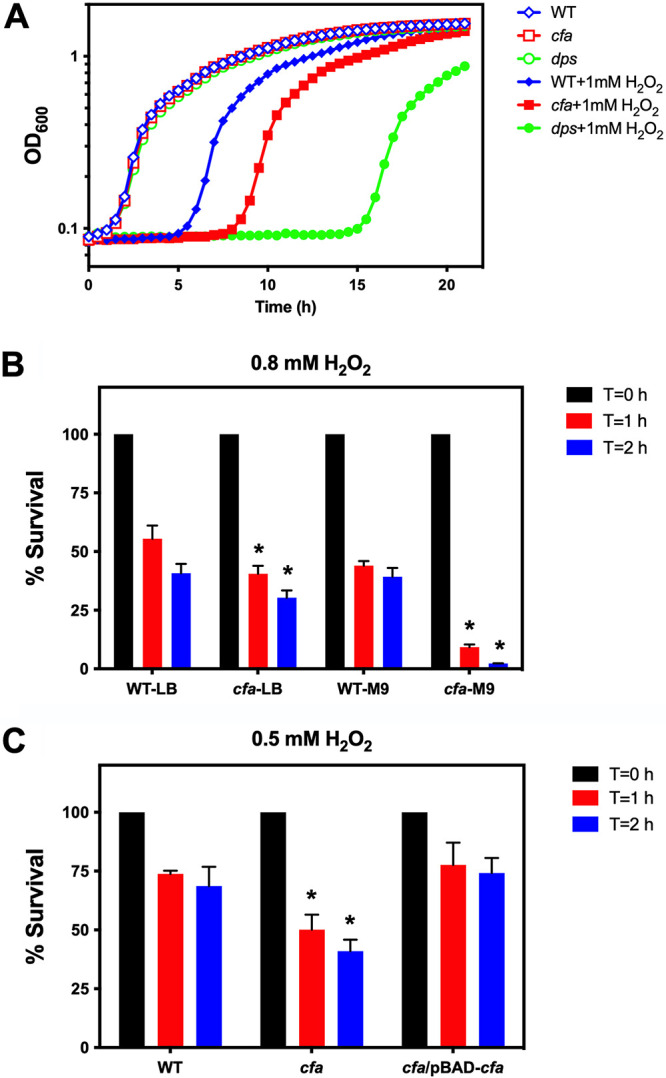
Cyclopropane fatty acids are important for are important for protection against hydrogen peroxide exposure. (A) S. Typhimurium strains that lack cyclopropane fatty acids are susceptible to growth inhibition by hydrogen peroxide. Stationary-phase S. Typhimurium strains were diluted to a final optical density (OD600) of 0.002 in LB medium (LB), and cell growth was monitored by OD600 at 37°C for 21 h (wild type, open blue diamonds; cfa mutant, open red squares; dps mutant, open green circles). Strains were also monitored for cell growth in LB medium with the addition of 1 mM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (wild-type, blue closed diamonds; cfa mutant, red closed squares; dps mutant, green closed circles). (B) Cyclopropane fatty acids are important for survival in hydrogen peroxide. Stationary-phase S. Typhimurium strains (wild-type and cfa mutant) were grown in LB medium or in M9 medium (M9) with 0.4% glucose and diluted in PBS, containing 0.8 mM H2O2, for 2 h at 37°C. CFU of surviving cells were determined post-H2O2 challenge at T = 0 (black bars), T = 1 h (red bars), and T = 2 h (blue bars). A Student’s t test was performed between the wild type and the cfa mutant at each time point. An asterisk (*) indicates P < 0.05. (C) The plasmid pBAD-cfa could complement a cfa mutant for survival in hydrogen peroxide. Stationary-phase S. Typhimurium strains (wild-type, cfa mutant, and cfa/pBAD-cfa) were grown in LB medium with 0.2% arabinose and incubated in PBS, containing 0.5 mM H2O2, for 2 h at 37°C. CFU of surviving cells were determined post-H2O2 challenge at T = 0 (black bars), T = 1 h (red bars) and T = 2 h (blue bars). A Student’s t test was performed between wild-type and cfa mutant or cfa/pBAD-cfa strains at each time point. An asterisk (*) indicates P < 0.05.
