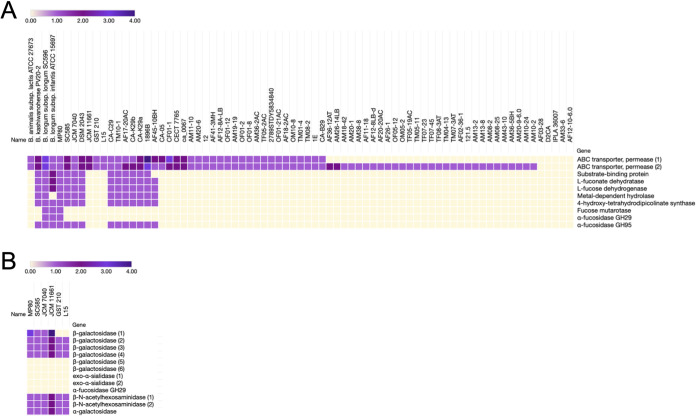
FIG 4.
(A) Relative abundance of fucosidase operon homologs in publicly available B. pseudocatenulatum genomes. Color gradient represents the number of homologs of each gene predicted within the genomes depicted. Hierarchical clustering (Spearman rank correlation, average linkage) was performed based on the presence or absence of homologs throughout the fucosidase operon. B. animalis subsp. lactis ATCC 27673 (F-HMO+), B. kashiwanohense PV20-2, B. longum subsp. longum SC596 (F-HMO positive [F-HMO+]), and B. longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15697 (F-HMO+) included for reference. B. pseudocatenulatum strain genome sequence accessions used are listed in Table S3 in the supplemental material. (B) Additional HMO-related glycosyl hydrolases and transporters from the six B. pseudocatenulatum strains glycoprofiled in this work (see Fig. 1 and 2). Homologs were predicted with PyParanoid (v0.4.1).