Figure 2. Aurora A inhibitors at higher concentrations antagonize their own cytotoxic activity and restore growth.
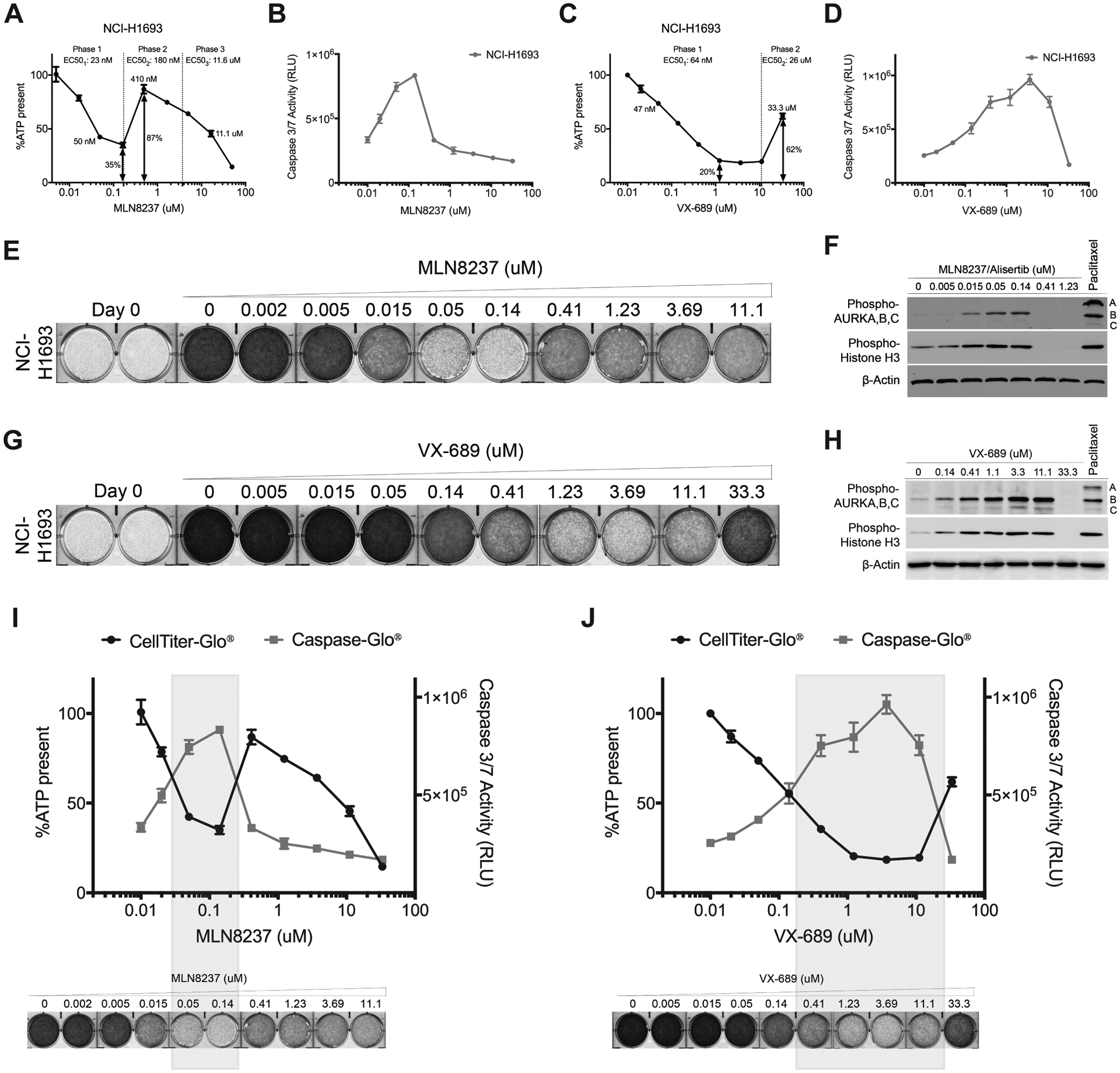
A, NCI-H1693 cells were treated with serial concentrations of MLN8237 for four days and cell viability was measured with a CellTiter-Glo assay, which measures ATP. B, NCI-H1693 cell line was treated with serial concentrations of MLN8237 for two days and active apoptosis was measured with a CaspaseGlo 3/7 assay. C, D, CellTiter-Glo and CaspaseGlo 3/7 assays were repeated with VX-689 treatments. Data are means of triplicate biological replicates with s.d. Some error bars are smaller than the data symbols. E, NCI-H1693 cells were treated with serial concentrations of MLN8237 or G, VX-689 for seven days and cell growth quantified with a crystal violet staining assay. F, Cell lysates of NCI-H1693 cell line were collected 48-hours after treating with MLN8237 or H, VX-689 and immunoblotted to measure phosphorylated histone H3 and phosphorylated Aurora A, B, and C. Paclitaxel was used in both sets of immunoblots as positive control and β-Actin was used as internal immunoblotting control. I, J, Overlay of cell viability, caspase 3/7 activity and crystal violet staining images with immunoblotting results at Aurora A kinase selective and non-selective (pan-Aurora kinase) inhibitory concentrations of MLN8237 and VX-689.
