Figure 6. Loss of Aurora kinase signaling allows cells to grow into polyploid giant cancer cells.
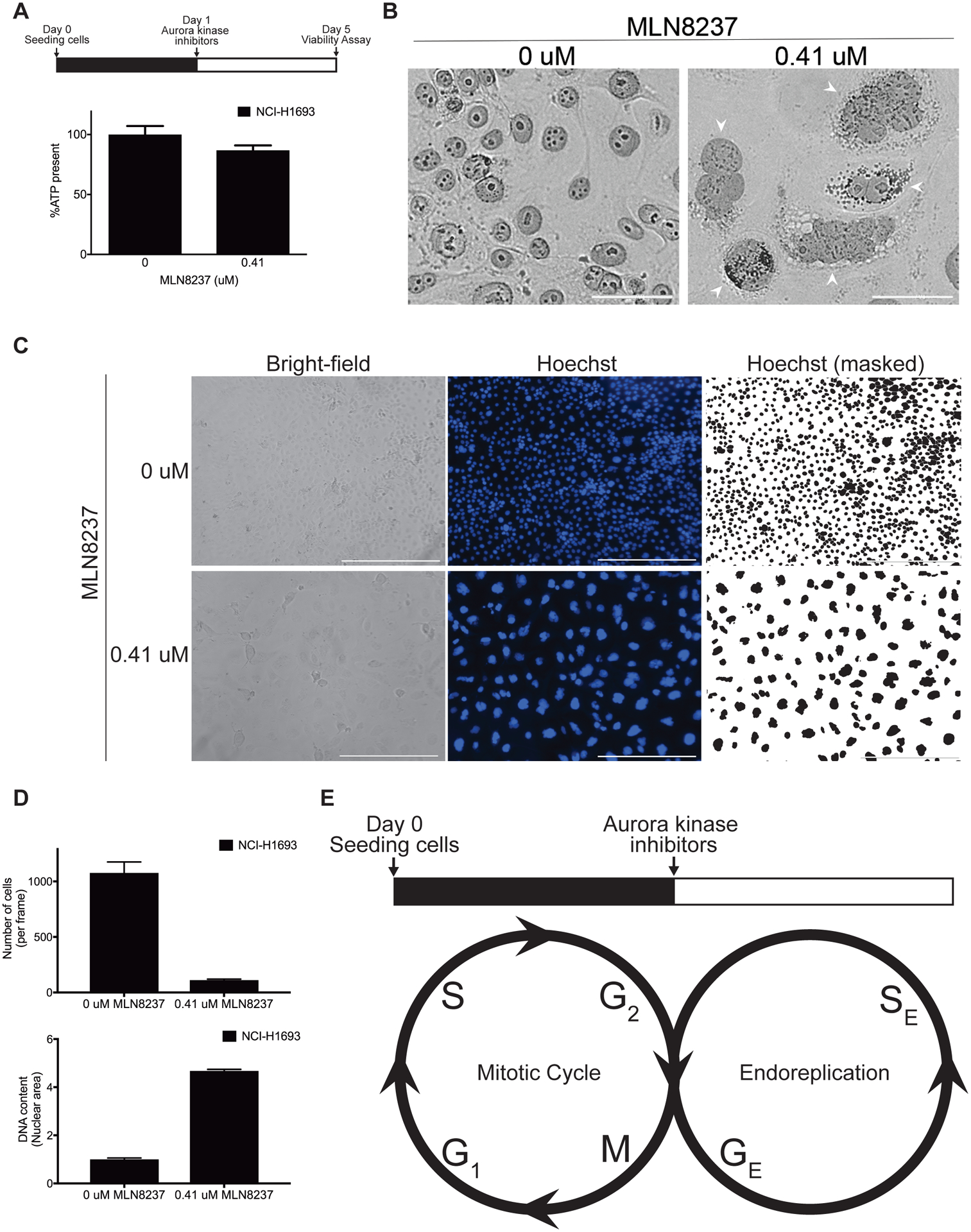
A, NCI-H1693 cells were treated with 0.41 μM of MLN8237 for four days and the ATP present was measured with a CellTiter-Glo assay. B, NCI-H1693 cells were treated with DMSO or 0.41 μM of MLN8237 for four days, stained with monoclonal antibodies against Lamin A/C and visualized with bright field or fluorescent microscopy. To provide detailed views of nuclear morphology (Arrowheads), merged images filtered for magenta light wavelengths were presented (Scale bar, 50 μM). C, NCI-H1693 cells were treated with 0.41 μM of MLN8237 for four days and visualized with bright-field or fluorescent microscopy at 10X magnification. Hoechst reagent was used to visualize the nuclei (Scale bar, 400 μM). D, The numbers of cells and their mean nuclear area from treated and untreated control samples are graphed. E, A proposed model of an endoreplication induced with the loss of Aurora kinase signaling. GE: Growth (G) phase in endoreplication, SE: Synthesis (S) phase in endoreplication.
