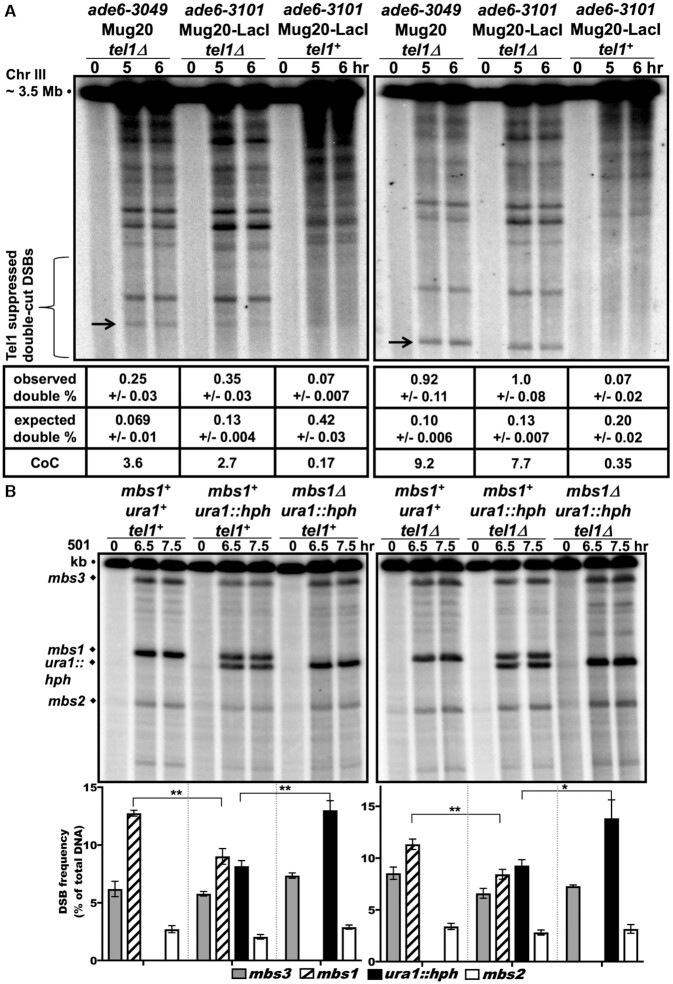
Figure 4.
The ade6-3101 hotspot manifests Tel1-dependent DSB interference; Tel1-independent DSB competition indicates separate mechanisms. rad50S strains were induced for meiosis, and DNA analyzed as in Figure 3, except meiosis was at 25°C in (B). (A) Both ade6-3049 and ade6-3101 manifest Tel1-dependent DSB interference. DNA was digested with NotI and analyzed on four to six blots with a probe between ade6 and the 75R DSB hotspot (left panel) or between ade6 and the tel1L hotspot near tel1 (right panel). Double-cut DSBs (black arrows; 75 kb left and 40 kb right) were evident in tel1Δ (left and middle lane sets) but not in tel1+ (right lane set). Coefficients of coincidence (CoC; mean ± SEM) show positive DSB interference (1 - CoC) in tel1+ and negative interference in tel1Δ. Single-cut DSBs and frequencies are visible in Supplementary Figure S3 using a different radioactive probe. (B) DSB competition at mbs1 is Tel1-independent. DNA was digested with NotI and analyzed on three to seven blots with a probe at the left end of the 501 kb NotI fragment J. DSBs at both mbs1+ and ura1::hph hotspots were reduced in the presence of the other hotspot (compare the double hotspot in the middle lane set to either single hotspot; **P = 0.007 for mbs1+ and **P = 0.0034 for ura1::hph), indicating mutual DSB competition. This competition was also present without Tel1 (right panel; **P = 0.002 for mbs1+ and *P = 0.018 for ura1::hph).