Figure 7.
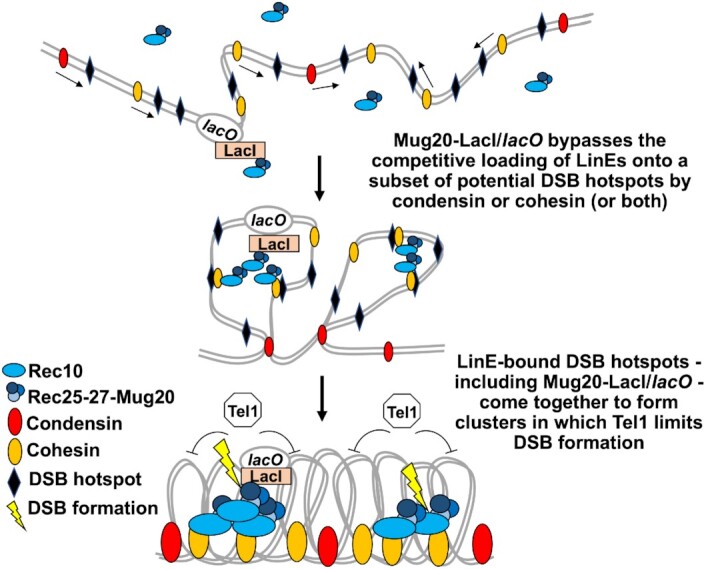
Model for DSB competition arising from the competitive loading of LinE complexes onto DSB hotspots. A loader, such as cohesin or condensin, moves along paired sister chromatids (thin black arrows) and loads LinE complexes (blue circles and ovals) onto a limited number of potential DSB hotspot sites. This prevents other sites in this traversed interval from being bound by LinEs and therefore limits DSBs to only the LinE-loaded sites (DSB competition). The ade6-3101 hotspot with a lacO array allows independent loading of Mug20-LacI and thus lacks DSB competition. The loader (cohesin or condensin) groups the LinE-hotspot complexes, including the Mug20-LacI-bound site, into a cluster, in which a DSB is formed. This DSB activates Tel1 protein kinase to prevent further DSB formation in that cluster (DSB interference).
