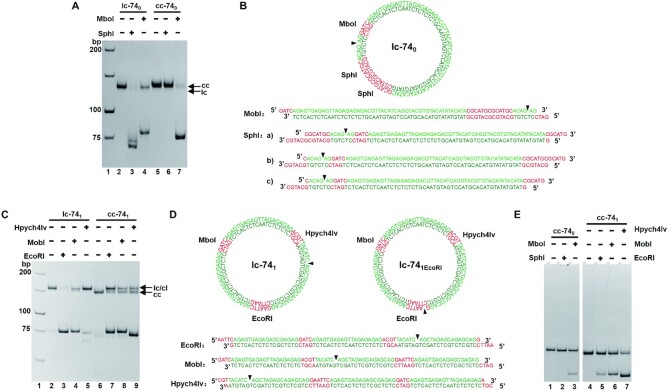
Figure 6.
Analysis of the positions of left-handed DNA in the LR-chimeras (8% PAGE). (A) Cleavage (5 min) of lc-740 and cc-740. Lane 2: lc-740; lanes 3 and 4: lc-740 cleaved by SphI and MobI, respectively; lane 5: cc-740; lanes 6,7: cc-740 cleaved by SphI and MobI, respectively. (B) Schematic illustration of lc-740 and linear products of cleavage by SphI and MobI, respectively. (C) Cleavage (5 min) of lc-741 and cc-741. Lane 2: lc-741; lanes 3–5: lc-741 cleaved by EcoRI, MobI, and Hpych4Iv, respectively; lane 6: cc-741; lanes 7–9: cc-741 cleaved by EcoRI, MobI, and Hpych4Iv, respectively. (D) Schematic illustration of lc-741, lc-741EcoRI and linear products of cleavage by EcoRI, MobI, and Hpych4Iv, respectively. (E) Cleavage (30 min) of cc-740 and cc-741 after binding to Z22. Lane 1: Z22 bind to cc-740; lanes 2, 3: Cleavage of cc-740 by SphI and MboI after binding to Z22, respectively; lane 4: Z22 bind to cc-741; lanes 5–7: Cleavage of cc-741 by EcoRI, MboI, and Hpych4Iv after binding to Z22, respectively.