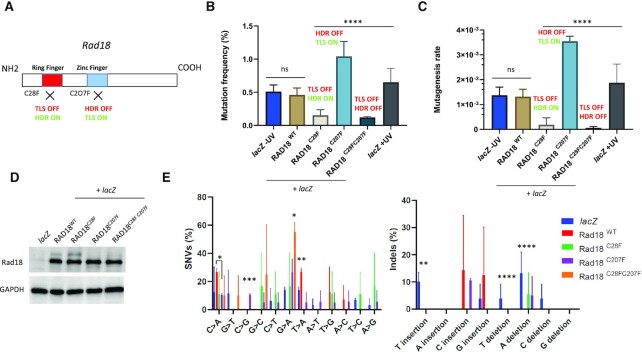
Figure 2.
Differential contribution of Rad18 to mutagenesis in pre-MBT Xenopus embryos. (A) Schematic illustration of Rad18 domains in DNA damage tolerance and repair. TLS depends on the ring finger domain, while HDR is dependent on the zinc finger domain. The C28F mutation knocks out TLS activity (TLS OFF), while the C207F mutation knocks out HDR activity (HDR OFF). (B) Mutation frequency and (C) mutagenesis rate (measured as described in Figure 1) of lacZ recovered from embryos co-injected with the indicated RAD18 mRNAs, or lacZ injected alone. The mutation frequency of lacZ recovered from embryos injected with a post-MBT amount of plasmid DNA (post-MBT) is also included as comparison. RAD18WT and RAD18C28F, n = 3; RAD18C207F and RAD18C28FC207F, n = 2. (D) Western blot of total protein extracts obtained from Xenopus embryos subjected to the indicated experimental conditions (n = 3). (E) Mutation spectrum of lacZ recovered from embryos injected with the indicated RAD18 variants, or lacZ injected alone. Data are presented as means ± SD. Means were compared using analysis of one-way ANOVA, followed by unpaired Student’s t-test.