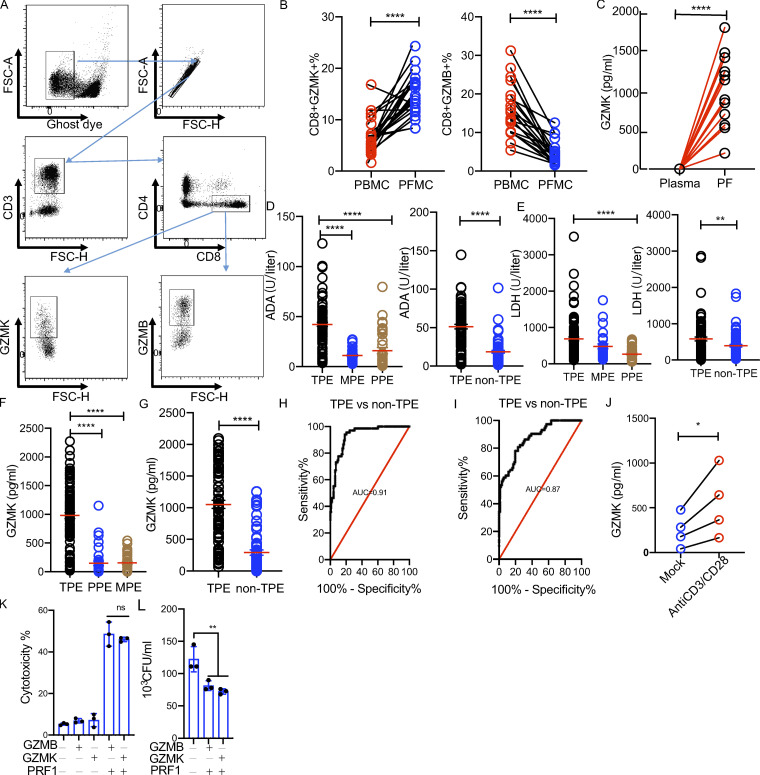
Figure 6.
GZMK is produced in PF of TPE patients and is inducible in CD8 T cells upon activation in vitro. (A) Gating strategy of GZMK+ or GZMB+ CD8 T cells by flow cytometry. FSC, forward scatter. (B) The frequency of GZMK+ CD8 or GZMB+ CD8 T cells in paired PBMCs and PFMCs from TPE patients (n = 22). A paired t test was used to analyze differences in paired samples; ****, P < 0.0001. (C) The level of GZMK protein expression in paired plasma and PF samples (n = 12); A paired t test was used to analyze differences in paired samples; ****, P < 0.0001. (D) The level of ADA in the PF from TPE, PPE, MPE, and non-TPE patients. Left: Cohort III (TPE, n = 98; PPE n = 36; and MPE n = 31). Right: Cohort IV (TPE, n = 88; and non-TPE, n = 73); One-way ANOVA Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test was used to compare differences among multiple groups; ****, P < 0.0001; unpaired t test was used to analyze differences between two groups; ****, P < 0.0001. (E) The level of ADA in the PF from TPE, PPE, MPE, and non-TPE patients. Left: Cohort III. Right: Cohort IV. One-way ANOVA Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test was used to compare differences among multiple groups; ****, P < 0.0001; unpaired t test was used to analyze differences between two groups; **, P < 0.01. (F) The level of GZMK protein in the PF from TPE, PPE, and MPE patients in cohort III. (G) The level of GZMK protein in the PF from TPE and non-MPE patients in cohort IV. One-way ANOVA Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test was used to compare differences among multiple groups; ****, P < 0.0001; unpaired t test was used to analyze differences between two groups; ****, P < 0.0001. (H) Receiver operater characteristic curve for GZMK to separate TPE from non-TPE in cohort III. (I) Receiver operater characteristic curve for GZMK to separate TPE from non-TPE in cohort IV. (J) The level of GZMK protein in CD8 from PFMCs (n = 4) with or without anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation; unpaired t test was used to analyze differences between two groups; *, P < 0.05. (K) The cytotoxicity of GZMK and GZMB with or without perforin in THP-1–derived macrophages. Purified GZMK (10 µg/ml) and GZMB (10 µg/ml) with or without Perforin 1 were added to THP-1–derived macrophages. Cytotoxicity was determined by WST-1 assays; one-way ANOVA Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test was used to compare differences among multiple groups; ns, P > 0.05. (L) The bactericidal activity of GZMK and GZMB in Mtb-infected THP-1–derived macrophages. Purified GZMK (10 µg/ml) and GZMB (10 µg/ml) with or without perforin 1 were added to Mtb-infected macrophages. CFUs were determined in 24 h. The experiments were replicated three times. One-way ANOVA Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test was used to compare differences among multiple groups; **, P < 0.01. The data represent means ± SEM.