Figure 1.
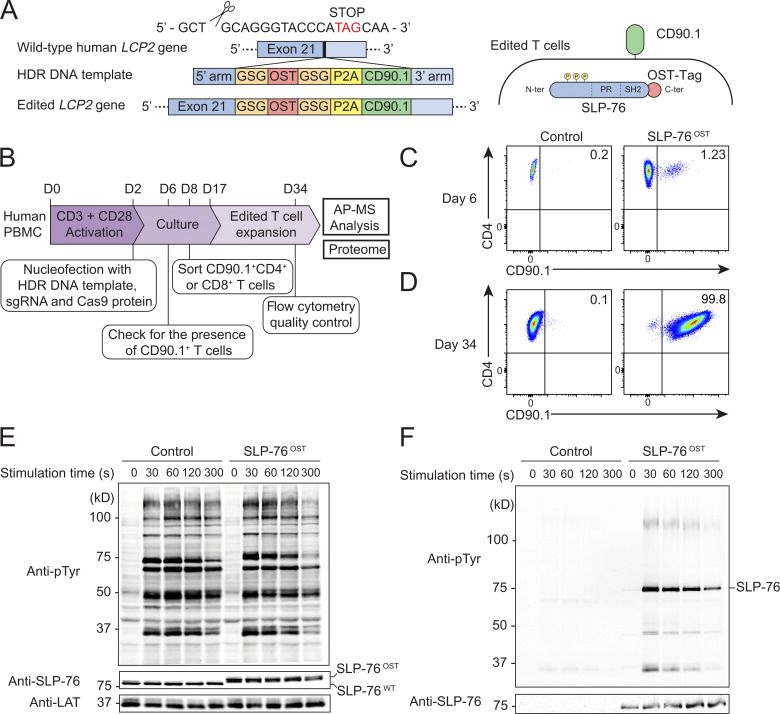
Human primary CD4+ T cells amenable to fast-track AP-MS characterization of the SLP-76 signalosome. (A) An sgRNA was designed to introduce a DSB 12 bp 5′ of the stop codon found in the human LCP2 gene that codes for SLP-76 (Table S1). An 845-bp-long dsDNA was used as a template for HDR (Table S2). After HDR, CD4+ T cells are expected to coexpress intracytoplasmic SLP-76OST molecules and the mouse CD90.1 protein at their surface. (B) Workflow used for editing, selecting, and expanding human primary CD4+ or CD8+ T cells expressing SLP-76OST molecules amenable to AP-MS. (C) CD4+ T cells nucleofected with Cas9 alone (control) or Cas9-sgRNA RNP plus the HDR DNA template (SLP-76OST edited) were analyzed 4 d after nucleofection by flow cytometry for CD90.1 expression. Data in C and D are representative of at least two experiments. (D) SLP-76OST–edited, CD90.1+CD4+ T cells were sorted, expanded in vitro, and analyzed for CD90.1 expression 1 d before AP-MS analysis, which corresponds to day 34 after the start of the culture. Also shown are control CD4+ T cells that were mock edited, sorted, and expanded in parallel. (E) Immunoblot analysis of equal amounts of proteins from total lysates of SLP-76OST–edited and control CD4+ T cells that were either left unstimulated (0 s) or stimulated for 30, 60, 120, or 300 s with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 and probed with antibody to phosphorylated tyrosine (anti–p-Tyr), anti–SLP-76, or anti-LAT (loading control). (F) Immunoblot analysis of equal amounts of lysates of SLP-76OST–edited and control CD4+ T cells stimulated as in E and subjected to affinity purification on Strep-Tactin Sepharose beads, followed by elution of proteins with D-biotin, and probed with antibody to phosphorylated tyrosine (anti–p-Tyr) or anti–SLP-76. Left margin in E and F, molecular size in kilodaltons. Data in E and F are representative of at least two independent experiments.