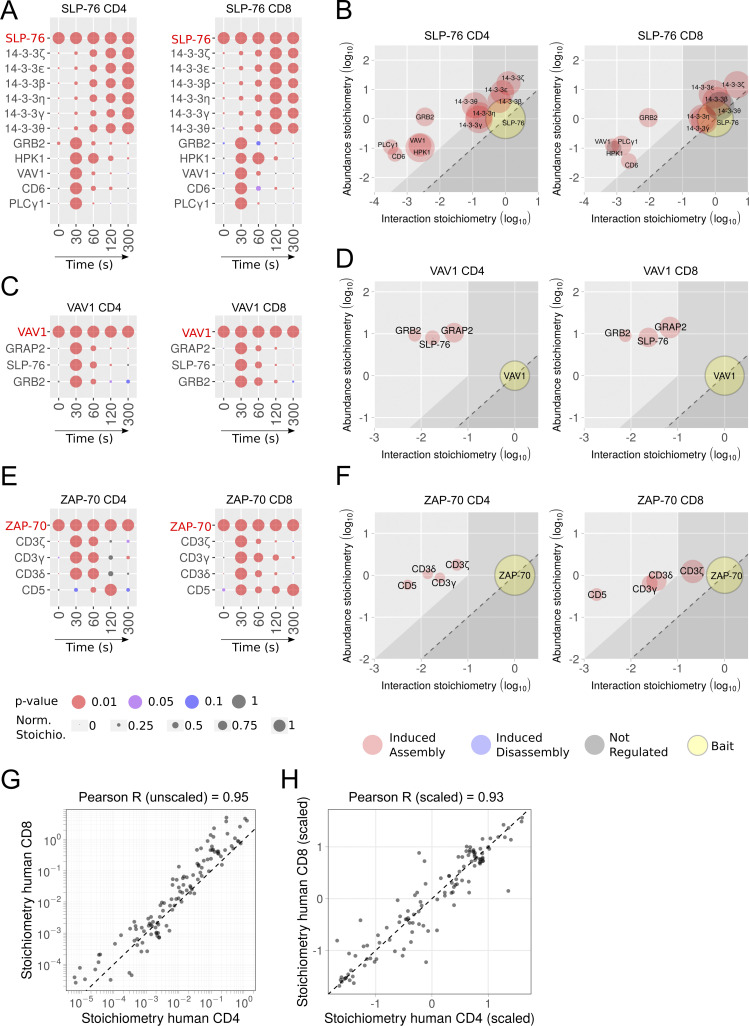
Figure 5.
Comparative analysis of the SLP-76, VAV1, and ZAP-70 interactomes of human primary CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (A) Dot plots showing the interaction stoichiometry of SLP-76 in human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells over the course of TCR-CD28 stimulation. In A–F, only the preys shared between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are shown. For A, C, and E, see description in Fig. 2 C. (B) Stoichiometry plots of the SLP-76 interactome of human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. For B, D, and F, see description in Fig. 2 D. (C) Dot plots showing the interaction stoichiometry of VAV-1 in human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells over the course of TCR-CD28 stimulation. (D) Stoichiometry plots of the VAV1 interactome of human CD4+ and CD8+ primary T cells. (E) Dot plots showing the interaction stoichiometry of ZAP-70 in human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells over the course of TCR-CD28 stimulation. The ZAP-70–CD3ε interaction occurring in CD8+ T cells is of high confidence (47-fold enrichment with a P value <0.05 at t = 30 s; Data S1). After slightly relaxing the cutoff values corresponding to ZAP-70–CD3ε interaction occurring in CD4+ T cells (4.3-fold enrichment with a P value <0.05 at t = 30 s; Data S1), a sixth interactor corresponding to CD3ε can also be added to the list of ZAP-70 interactors shared between mice and humans. (F) Stoichiometry plots of the ZAP-70 interactomes of human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (G) The interaction stoichiometries of TCR-regulated interactions identified in both human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and corresponding to the SLP-76, VAV1, and ZAP-70 baits were compared across all conditions of stimulation. (H) Same comparison as in G using scaled (Z-score) interaction stoichiometries to compare variations of interaction stoichiometries relative to their means. Also shown in G and H are the Pearson correlation coefficient and a dashed line corresponding to equal stoichiometries (G) or scaled stoichiometries (H). Scaling was performed for each interaction by subtracting the mean and dividing it by the SD of log-transformed stoichiometries across all conditions of stimulation.