Figure 2.
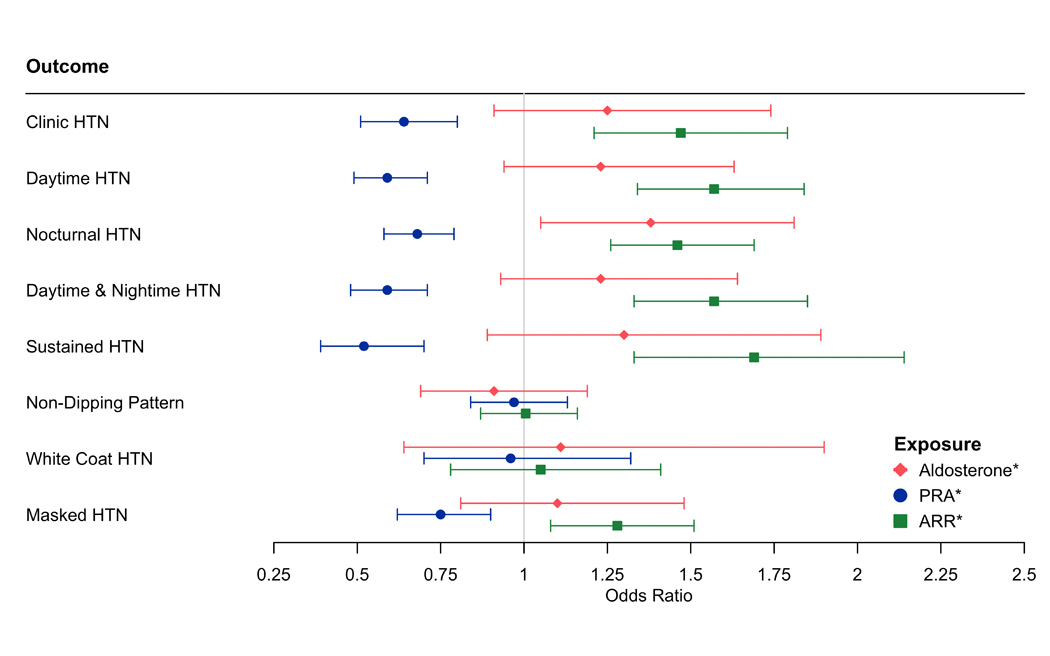
The Association of Log-Aldosterone, Log-Plasma Renin Activity and Log-Aldosterone: Renin Ratio with Ambulatory Blood Pressure Phenotypes
Model adjusted for age, sex, education and occupation, smoking, waist circumference, physical activity, low-density lipoprotein, history of cardiovascular disease, alcohol, diabetes, hormone replacement therapy, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and PRA or aldosterone (Table VI in the Supplement, Model 2)
* indicates log-transformed variable
Abbreviations: HTN = hypertension; PRA = plasma renin activity; ARR = aldosterone: renin ratio
Clinic Hypertension = clinic SBP ≥140 mmHg or clinic DBP ≥90 mmHg; Daytime Hypertension = daytime SBP ≥ 135 mmHg or daytime DBP ≥85 mmHg, Nocturnal Hypertension = night-time SBP ≥ 120 mmHg or night-time DBP ≥ 70 mmHg; Daytime & Nocturnal hypertension = combination of Daytime and Nocturnal Hypertension; Sustained hypertension = combination of Clinic and Daytime Hypertension; Non-Dipping Pattern = <10% decrease in mean awake vs mean asleep SBP; White Coat Hypertension = absence of Daytime Hypertension with presence of Clinic Hypertension, Masked Hypertension = presence of Daytime Hypertension with absence of Clinic Hypertension.
