Figure 5.
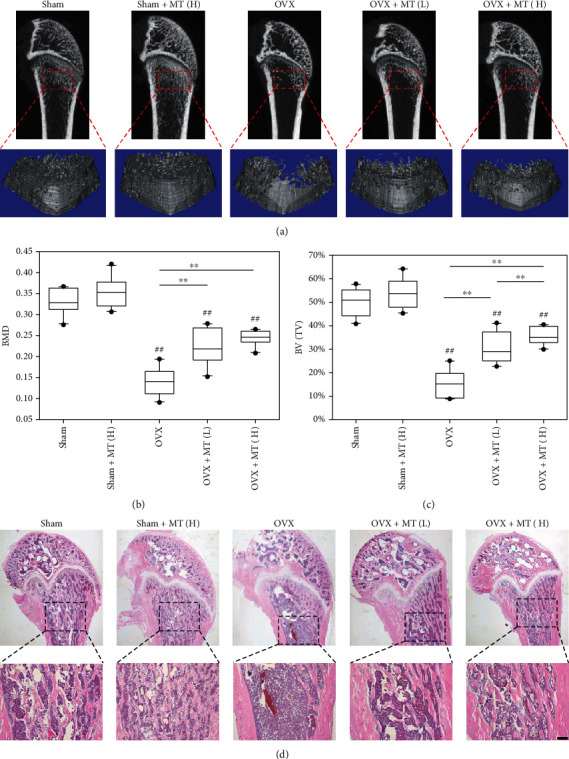
In vivo administration of melatonin protected the trabecular bone microstructure of OVX rats following estrogen withdrawal. After ovariectomy, melatonin (MT) was injected into OVX rats through the tail vein at a low dosage (1 mg/kg, OVX+MT(L)) or a high dosage (10 mg/kg, OVX+MT(H)), while sham-op rats were injected with melatonin at 10 mg/kg (sham+MT(H)). The sham and OVX rats received saline containing the same amount of ethanol. (a) Micro-CT and 3D reconstruction were used to histomorphometrically analyze the rat femurs. (b) The effect of melatonin administration on bone mineral density (BMD). (c) The effect of melatonin administration on bone volume ratio (BV/TV, %). (d) Representative histological images of rat femurs stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Scale bar = 200 μm. Values are presented as the mean ± S.E.M of ten samples in each group (n = 10) in micro-CT and 3D reconstruction assays. Statistically significant differences are indicated by ∗p < 0.05 or ∗∗p < 0.01 between the indicated groups; #p < 0.05 or ##p < 0.01 versus the sham group.
