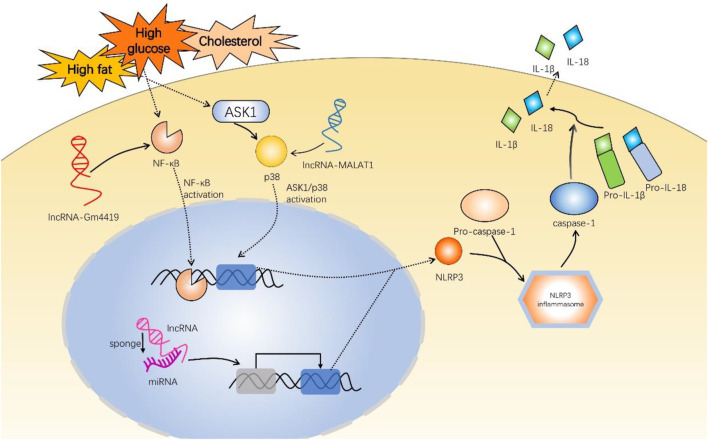
FIGURE 2.
Mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs involved in inflammatory responses of diabetic complications via NLRP3 inflammasome. These experiments used high-glucose induction to establish diabetic mouse models. LncRNA-Gm4419 activates NF-κB pathway to upregulate NLRP3 expression in DN. LncRNA-MALAT1 activates ASK1/p38 pathway to upregulate NLRP3 in DR. In addition, most lncRNAs, such as ANRIL, Kcnq1ot1, NEAT1, HCP5, SNHG16, H19, and HCG18 promote or inhibit NLRP3 expression by sponging miRNA and regulating downstream target genes. NLRP3 and pro-caspase-1 are indispensable to NLRP3 inflammasome assembly. NLRP3 inflammasome activates pro-caspase-1 into caspase-1, promoting IL-1β and IL-18 generation. NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; miRNA, microRNA; ANRIL, antisense noncoding RNA in the INK4 locus; Kcnq1ot1, Kcnq1 overlapping transcript 1; NEAT1, nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1; HCP5, HLA complex P5; SNHG16, small nucleolar RNA host gene 16; HCG18, HLA complex group 18.