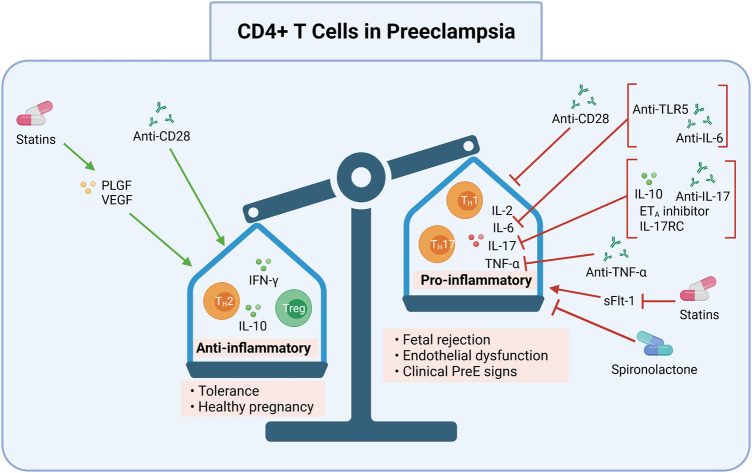
FIGURE 2.
CD4+ T cell pro-inflammation and processes may be targeted in preeclampsia. Induction of anti-inflammatory CD4+ T cells (Th2s) and Tregs, and inhibition of pro-inflammatory CD4+ T cells (Th17s, TH1s) may be one pathway for preeclampsia treatment and prevention. Collectively, modulation of these processes may ameliorate the overly pro-inflammatory immune response in preeclampsia. Shifting the ratio of pro-to anti-inflammatory CD4+ T cells may prevent preeclampsia by allowing proper placentation and reducing resultant oxidative stress. This can be done by 1) promoting an anti-inflammatory milieu (Th2, Treg, IFN-γ, IL-10) with anti-CD28, statins that induce PLGF and VEGF, or 2) inhibiting a pro-inflammatory milieu (Th1, Th17, IL-2, IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α) with anti-CD28 or spironolactone, or inhibiting sFlt-1using statins. Specific cytokines may also be inhibited, such as IL-6 by anti-TLR5 or anti-IL-6; IL-17 by IL-10, ETA inhibitors, IL-17RC, and anti-IL-17; or TNF-α by anti-TNF-α. The anti-inflammatory CD4+ T cell response may result in tolerance and a healthy pregnancy while the pro-inflammatory CD4+ T cell response may lead to fetal rejection, endothelial dysfunction, and clinical preeclampsia signs. DC, dendritic cells; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies; Th, Helper T cell; Treg, regulatory T cell; IL, interleukin; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; anti, antibody; ETA, endothelin-1 receptor A; sFlt-1, soluble Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase-1; PLGF, placental growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; IL-17RC mouse IL-17 receptor C; TLR5, toll like receptor 5. Created with https://biorender.com.