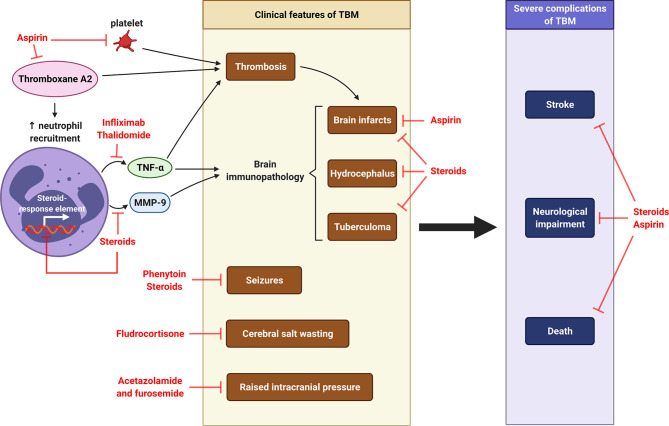
Figure 8.
Host-directed therapy in CNS-TB. Pro-coagulant thromboxane A2 causes thrombosis and subsequent formation of brain infarcts. It also increases the recruitment of neutrophils, which releases TNF-α and MMP-9, two major mediators contributing to brain immunopathology of TBM, including brain infarcts, hydrocephalus and tuberculoma. Other clinical features of TBM are cerebral salt wasting, seizures and raised intracranial pressure. Severe complications of TBM are stroke, neurological impairment and death. Aspirin is used to inhibit thromboxane A2, prevent brain infarcts and reduce stroke and mortality (245, 246). Thalidomide is TNF-α antagonist functions to reduce thrombosis and brain immunopathology in TBM (11). Corticosteroid dexamethasone can inhibit MMP-9 secretion and further reduce the consequent brain immunopathology (10, 247), while fludrocortisone can improve cerebral salt wasting (248). The use of steroid may therefore reduce neurological impairment and death. The anti-seizure phenytoin is taken to control seizures in TBM, while the diuretics acetazolamide and furosemide can be used to manage raised intracranial pressure in TBM (249). Illustration created with Biorender.com.