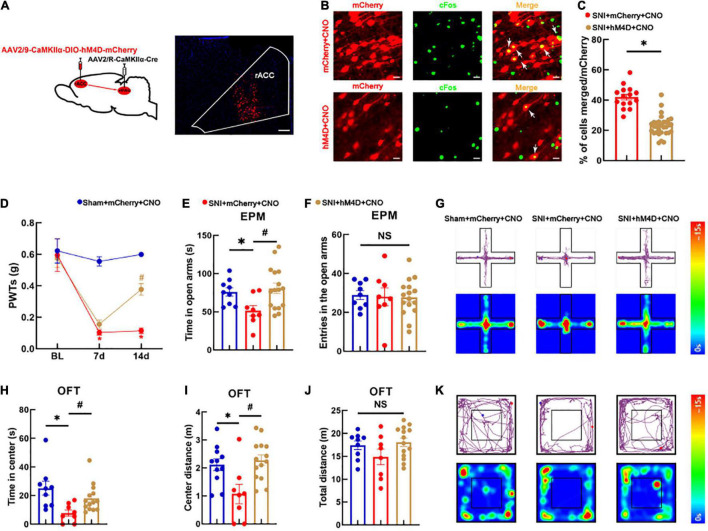
FIGURE 3.
Specific inhibition of the rACC-vlPAG neural circuit relieves hyperalgesia and anxiety-like behaviors in SNI mice models. (A) The left side shows a schematic diagram of chemogenetics, and the right side shows a representative image of viral expression within the rACC. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Representative images of the glutamatergic neurons (red) in the rACC that co-localize with c-Fos. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Percentage of co-localization of the glutamatergic neurons and c-Fos in each group (n = 15 slices from three mice, *P < 0.05). (D) Time course of the SNI-induced changes in the PWTs. (E) Time spent in the open arms in the EPM test. (F) The entries in the open arms show no significant difference among the three groups. (G) Representative movement trajectory diagram and activity heatmap of the mice in the EPM test for each group. (H) Time spent in the center of the field by the mice in the OFT. (I) Center distance in the OFT. (J) There is no significant difference in the total distance covered by the mice in the OFT among the three groups. (K) Representative movement trajectory diagram and activity heatmap of the significant mice in the OFT for each group. Data are presented as means ± standard errors of the means. *P < 0.05 vs. the sham + mCherry + CNO group; #P < 0.05 vs. the SNI + mCherry + CNO group; NS, not significant. n = 8–16 mice per group in (D–F); n = 8–14 mice per group in (H–J).