Fig. 1.
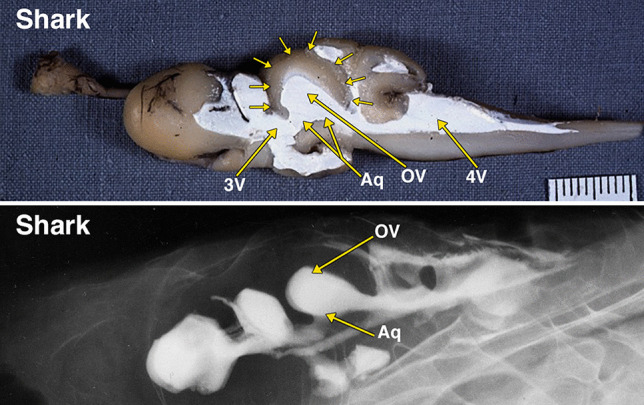
Dissected brain of a shark with radiopaque barium-gelatin-contrast filled cerebral ventricles. The midsagittal dissection (Fig. 1) demonstrates a relatively large, thin-walled optic lobe, outlined by multiple small arrows, that includes a large optic ventricle (OV). The midbrain ventricle (Aq) and optic ventricles form a large continuous cavity. The comparative anatomy literature uses the term aqueduct for the midbrain ventricle in all vertebrates with a cerebral ventricular system. The lateral radiograph of the entire dissected brain demonstrates both superimposed optic ventricles (OV) and the aqueduct (Aq). Additional abbreviations: 3 V, 3d ventricle; 4 V, 4th ventricle. The distance between 2 black lines on the ruler in the specimen photograph is 1 mm
