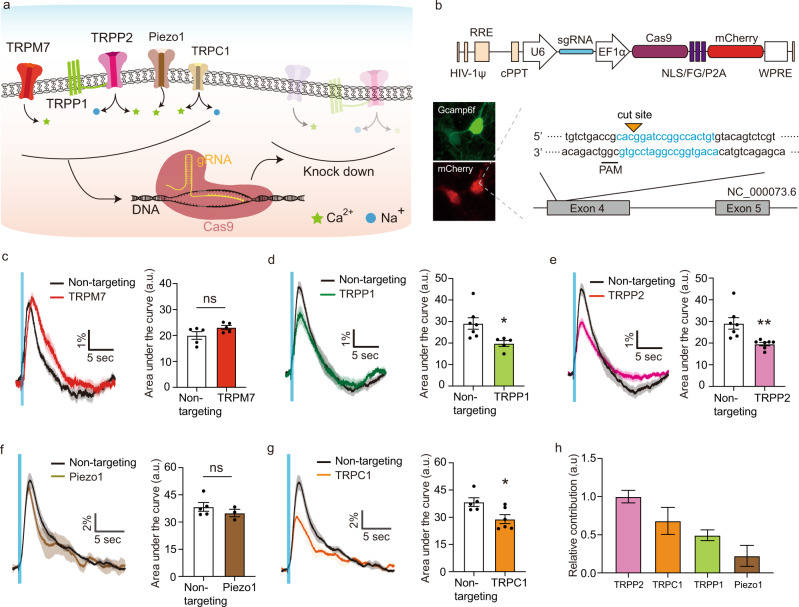
Fig. 5. CIRSPR/Cas9 knockdown of mechanosensitive ion channels.
a Schematic of the strategy to knockdown individual ion channels using CRISPR/Cas9. b Schematic of the gene construct for the CRISPR knockdown. A sgRNA was designed to target each channel and delivered to neurons via lentivirus. c Calcium responses from wild-type neurons and neurons treated with CRISPR/Cas9 for TRPM7 knock down (n = 5 independent experiments each, Unpaired t-test, two-tailed, p = 0.1073). d Calcium responses from wild type neurons and modified neurons with CRISPR/Cas9 for TRPP1 knock down (n = 7 independent experiments for control, and five independent experiments for TRPP1, Unpaired t-test, two-tailed, p = 0.0208). e Calcium responses from wild type neurons and modified neurons with CRISPR/Cas9 for TRPP2 knock down (n = 7 independent experiments each, Unpaired t-test, two-tailed, p = 0.0084). f Calcium responses from wild type neurons and modified neurons with CRISPR/Cas9 for Piezo1 knock down (n = 5 independent experiments for control, and three independent experiments for Piezo1, Unpaired t-test, two-tailed, p = 0.3727). g Calcium responses from wild type neurons and modified neurons with CRISPR/Cas9 for TRPC1 knock down (n = 5 independent experiments for control, and 6 independent experiments for TRPC1, Unpaired t-test, two-tailed, p = 0.0232). h Relative contribution of each channel to the ultrasound-evoked calcium response (normalized ΔΔF/CRISPR efficiency, n = 7 (TRPP2), 6 (TRPC1), 5 (TRPP1), 3 (Piezo1)). Control is non-targeting sgRNA. Mean trace is solid and SEM is shaded in time courses. Bar graph values represent mean ± SEM.