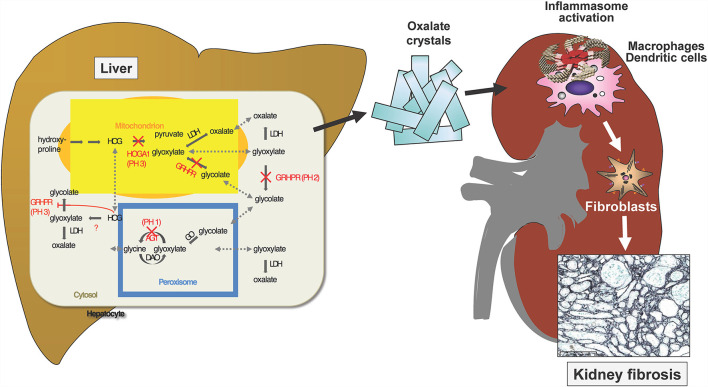
Figure 4.
Three known gene defects in hepatocytes cause oxalate accumulation in primary Hyperoxaluria I-III. Ca-Oxalate crystals precipitate in the kidney where water gets reabsorbed and the solubility coefficient of this salt is exceeded. The crystals activate the inflammasome in renal macrophages and dendritic cells, which stimulate interstitial fibroblasts to deposits collagen, resulting in kidney fibrosis.