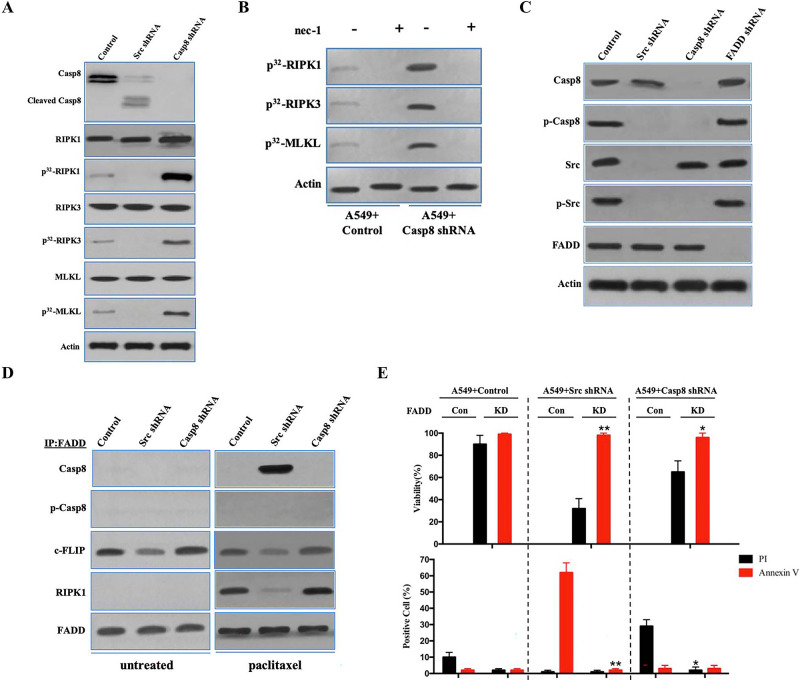
Figure 4.
FADD interacted with caspase 8, c-FLIP, and RIPK1 to induce cell death signaling following paclitaxel treatment. (A) Immunoblotting analysis of caspase 8, cleaved caspase 8, RIPK1, RIPK3, MLKL, and β-actin in A549 cells with control/c-Src/caspase 8 shRNA treated by 200 nM paclitaxel for 48 h after 48-h attachment on the fibronectin-coated dish. Cells were labeled with [32P]-orthophosphate. Phosphorylated RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL were measured by Cyclone Plus Phosphor Imager. (B) A549 cells with control/caspase 8 shRNA were treated by 200 nM paclitaxel with or without nec-1 for 48 h after 48-h attachment on the fibronectin-coated dish. Cells were labelled with [32P]-orthophosphate. Phosphorylated RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL were measured by Cyclone Plus Phosphor Imager. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of caspase 8, p-Casp8, c-Src, p-Src, FADD, and β-actin in A549 cells with control/c-Src/caspase 8/FADD shRNA after 48-h attachment on the fibronectin-coated dish. (D) The immunocomplexes of A549 cells with control/c-Src/caspase 8 shRNA treated with or without 200 nM paclitaxel for 48 h after 48-h attachment on the fibronectin-coated dish were eluted with antibody against FADD, and whole elution was used to measure caspase 8, p-Casp8, c-FLIP, and RIPK1. (E) A549 cells with control/c-Src or caspase 8 shRNA combined with or without FADD knockdown were treated with 200 nM paclitaxel for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by measuring ATP levels using Cell Titer-Glo kit. Data were represented as mean ± standard deviation of duplicates. Cells were analyzed for annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining by flow cytometry. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results. *p < 0.05 versus control, **p < 0.01 versus control.