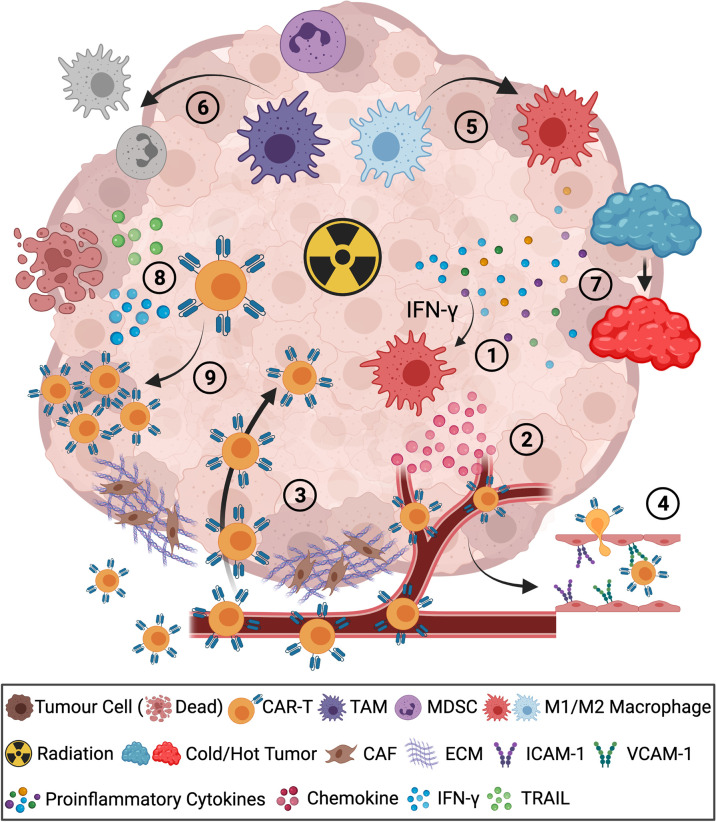
Figure 1.
Radiotherapy improves the outcomes of CAR-T cells in combination therapy. ①Radiation-induced IFN-γ promotes chemokine secretion of CXCL9/10/11, ②leading to effective CAR-T cell homing to the tumor bed. ③Diminished tumor barriers of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) and extracellular matrix (ECM) promote CAR-T cell infiltration. ④Radiation-induced expression of ICAM-1/VCAM-1 on the endothelium of tumor vasculature facilitated CAR-T cell infiltration. ⑤RT polarized M2 macrophages to M1 macrophages in the TME. ⑥Reduction of TAM and MDSC by RT. ⑦Radiation-induced increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines altered the TME from immunosuppressive “cold” to immune-inflamed “hot”. ⑧Radiation enhanced infiltrated CAR-T cell function with increased expression of TRAIL, IFN-γ and ⑨augmented expansion of CAR-T cells. The figure is created with BioRender.com.