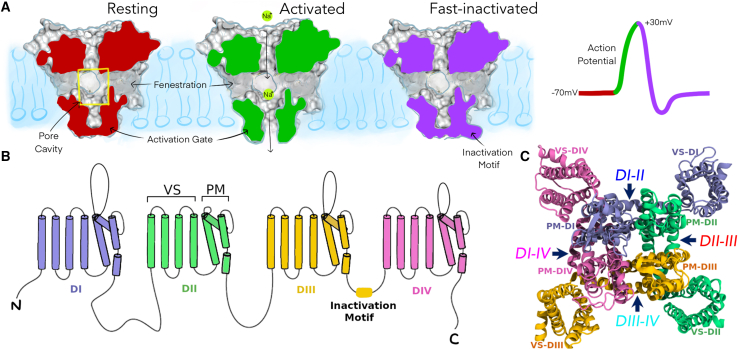
Figure 1.
Overview of voltage-gated sodium channel structure and function. (A) Cut-surface view of a eukaryotic sodium channel pore module (voltage sensors not shown here) in different states during an action potential: resting (red), activated (green), and fast-inactivated (purple); also, highlighting the location of pore cavity (yellow box) and fenestrations. (B) Topology of the pseudotetrameric eukaryotic sodium channel alpha-subunit showing each of the domains (DI-DIV) consisting of six transmembrane helices each (S1-S6). (C) Top-down view of the entire sodium channel depicting the voltage sensors (VS) wrapping around the pore module (PM) in a domain-swapped manner; fenestrations labeled by arrows.