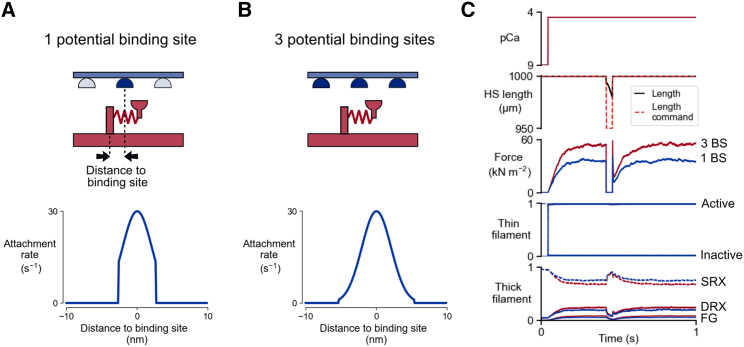
Fig. 8.
Slack/re-stretch maneuvers for different numbers of potential binding sites. (A) Myosin heads are allowed to bind to the nearest binding site (top). The gaussian attachment rate profile is thus zero outside of the nearest binding site distance range (bottom). (B) Myosin heads are allowed to bind to one of the three nearest binding sites (top). The gaussian attachment rate profile is thus wider than for the “1 potential binding site” case (bottom). (C) Slack/re-stretch protocols. The half-sarcomere length is suddenly shortened by 5%, then stretched back to its initial value. Immediately after the rapid shortening, the half-sarcomere shortens against zero load (force is zero). During the re-stretch, there is a sudden increase in force, followed by a force drop that does not reach zero (force residual). The isometric and residual forces are greater for simulations with 3 potential binding sites (red) than for 1 potential binding site (blue).