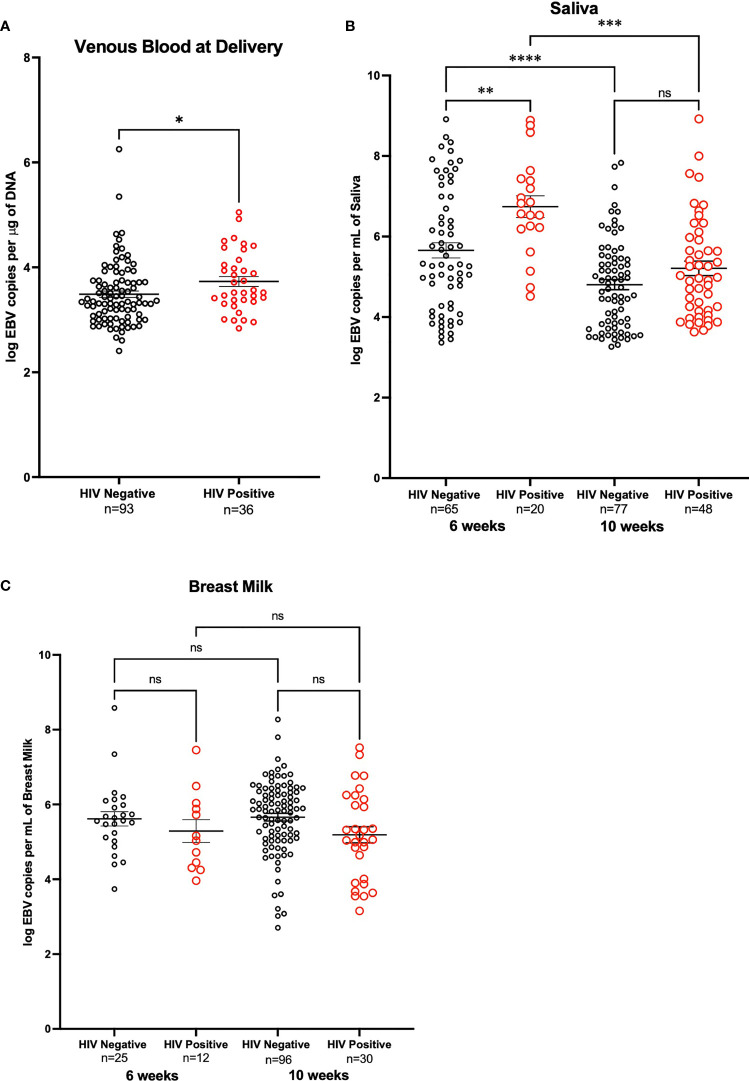
Figure 2.
EBV Viral load in HIV negative and positive mothers. (A) Maternal venous blood cell pellet at time of delivery. Analysis made on a zero-inflated model. DNA from venous blood from HIV- mothers (n=141) and HIV+ mothers (n=61) was tested for EBV viral load, only those who had detectable EBV are shown. HIV-mothers had a mean log EBV copies per μg of DNA of 3.49 and HIV+ mothers had a mean log EBV copies per μg of DNA of 3.73 (p-value = 0.04) (B) DNA from saliva from mother at 6-weeks post-partum that were HIV- (n=97) and HIV+ (n=52) (p-value < 0.01), as well as mothers at 10-weeks post-partum that were HIV- (n=103) and HIV+ (n=56) were tested for EBV shedding, only those that are positive shedders are shown. Comparison across time points account for the paired nature of the data and were analyzed with Wilcoxon signed rank exact test; differences among HIV+ (p-value < 0.01) and HIV- (p-value < 0.01) were observed. (C) Breast Milk DNA from mothers at 6- weeks post-partum both HIV- (n=25) and HIV+ (n=12) and breast milk of mothers 10-weeks post-partum HIV- (n=111) and HIV+ (n=34) were analyzed for shedding of EBV. Only mothers in which shedding was detected are shown. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001, ns, not significant.