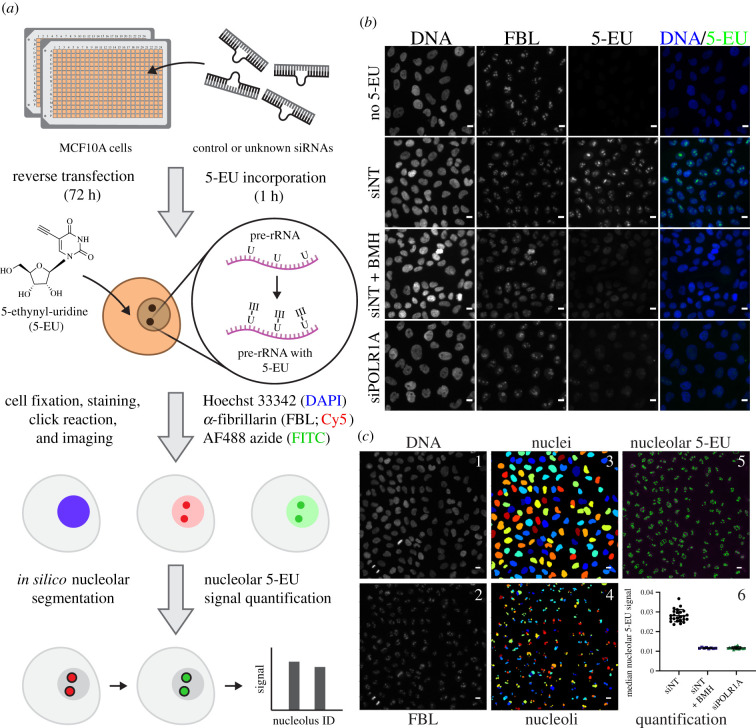
Figure 1.
A high-throughput assay for nucleolar rRNA biogenesis using 5-ethynyl uridine (5-EU). (a) Schematic of the 5-EU assay protocol. MCF10A cells are reverse-transfected in 384-well imaging plates with control or unknown siRNAs for 72 h. Following target depletion, 5-EU is incorporated into nascent RNA transcripts for 1 h, with the majority of label incorporated into nascent pre-ribosomal RNA (pre-rRNA). Treated cells are fixed and stained for DNA (Hoechst 33342, DAPI channel) and the nucleolar protein FBL (Cy5 channel). 5-EU in nascent transcripts is conjugated to an azide fluorophore (AF488 azide, FITC channel) via a copper-catalysed click reaction. After fluorescent imaging, cell nuclei and nucleoli are segmented in silico with CellProfiler, and nucleolar-specific 5-EU signal is quantified for each nucleolus object identified. (b) RNAP1 inhibition specifically inhibits nucleolar 5-EU incorporation. No 5-EU, experiment without 1 h 5-EU incorporation. Treatment with a non-targeting siRNA (siNT) leads to a high 5-EU signal within the nucleolus and moderate nucleoplasmic background signal. Acute treatment with BMH-21 (siNT + BMH) or siRNA-mediated depletion of POLR1A (siPOLR1A) decreases nucleolar 5-EU signal, although nucleoplasmic background remains. DNA (Hoechst staining), FBL (staining), 5-EU (5-EU staining) and DNA/5-EU (combined Hoechst and EU staining). Scale bars, 10 µm. (c) Schematic of CellProfiler segmentation and nucleolar 5-EU quantification. Panels 1 and 2, raw images of DNA and FBL staining. Panels 3 and 4, nuclei or nucleoli segmented by CellProfiler from DNA or FBL staining, respectively. Rainbow colouring identifies object number. Panel 5, overlay of segmented nucleoli (green) on top of 5-EU staining (magenta). Panel 6, quantification of median nucleolar 5-EU signal for nucleoli in cells treated with siNT, siNT and BMH-21, or siPOLR1A. n = 24, 8 or 16 wells, respectively. Scale bars, 10 µm.