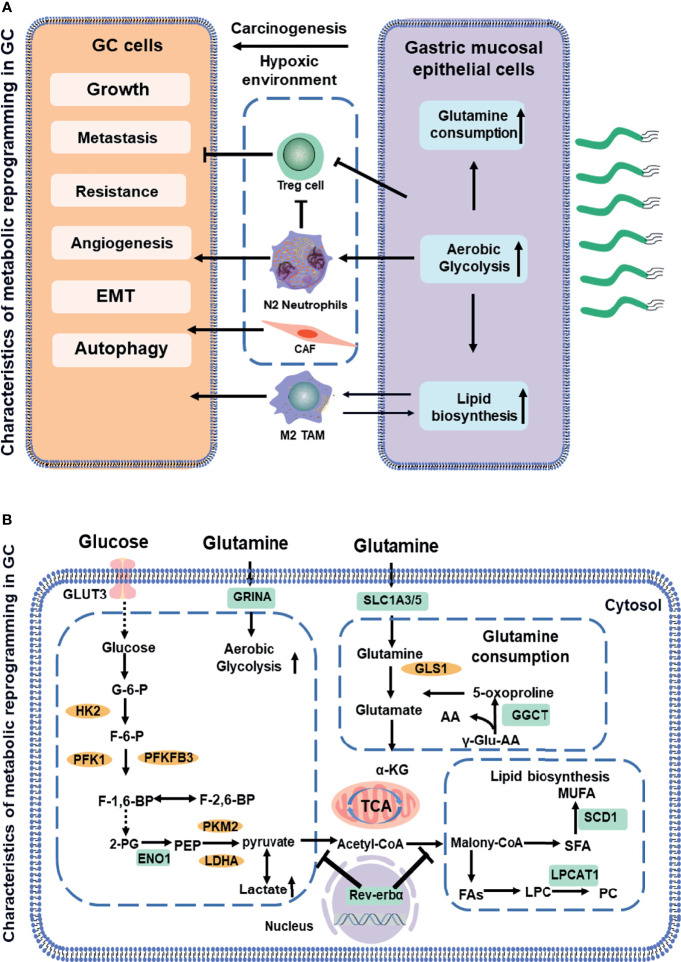
Figure 1.
Schematic showing a comparative account of normal vs. cancer cell metabolic reprogramming (A). The association between aerobic glycolysis (Warburg effect) and the glutamine metabolism and fatty acids metabolism. Biomarkers in GC (indicated in green boxes) along with signaling molecules (orange circles). Next, the mitochondrial dysfunction or phenotypic alteration (B). AA, amino acid; CoA, coenzyme A; ENO1, enolase 1; F-6-P, fructose 6-phosphate; FA, fatty acids; G-6-P, glucose-6-phosphate; GGCT, glutamylcyclo transferase; GLUT3, glucose transporter3; GRINA, glutamate receptor; GLS, glutaminase1; HK2, hexokinase2; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; LPCAT1, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase; MUFA, multiunsaturated fatty acid; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PFK1, phosphofructokinase1; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PFKFB3, phosphofructokinase-2/fructose-2,6 bisphosphatase 3; PKM2, pyruvate kinase2; SFA, saturated fatty acids; SCD-1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle. Dotted lines indicate the feed-back inhibition/regulation of some of the glycolytic enzymes by corresponding metabolites.