Fig. 3.
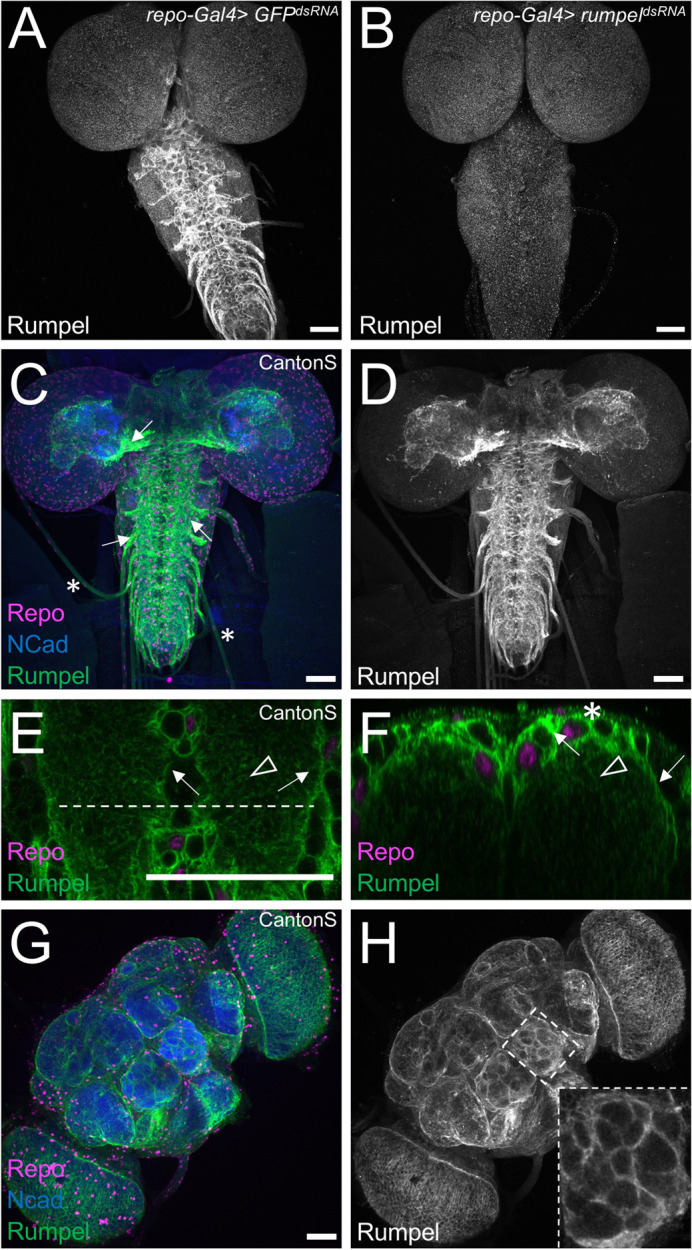
Rumpel protein is expressed in the neuropil-associated glial cells. All specimens are stained for Repo localization to define glial nuclei (magenta), for N-Cadherin localization to visualize axonal and dendritic cell membranes (blue) and for Rumpel protein localization (green/grey). (A–F) Third instar larval brains and (G,H) adult brain. (A) In control animals [repo-Gal4, UAS-GFPdsRNA] Rumpel protein localizes around the neuropil. (B) Upon expression of rumpeldsRNA in the all-glial cells [repo-Gal4, UAS- rumpeldsRNAv43922] no Rumpel protein can be detected, demonstrating the specificity of the anti-Rumpel antibody. (C,D) Rumpel localization is observed surrounding the neuropil (arrows) in a position of the ensheathing glial cells. Very little Rumpel protein is found along larval nerves (asterisks). (E) Image of a single confocal plane through a third instar larval ventral nerve cord. Rumpel localizes to ensheathing glial cell membrane (arrow) and to cell processes of astrocyte-like glial cells (arrowhead). The dashed line indicates the position of the orthogonal section shown in F. (F) Rumpel localizes to ensheathing glial cells (arrows) and astrocytic processes in the neuropil (arrowhead). Note, the pronounced cortex-glial cell like ramifications of the ensheathing glia dorsally to the neuropil (asterisk). (G,H) Rumpel localizes around the neuropil in adult brains at a position of the ensheathing glia (inset: antennal lobe). Scale bars: 50 µm.
