Fig. 6.
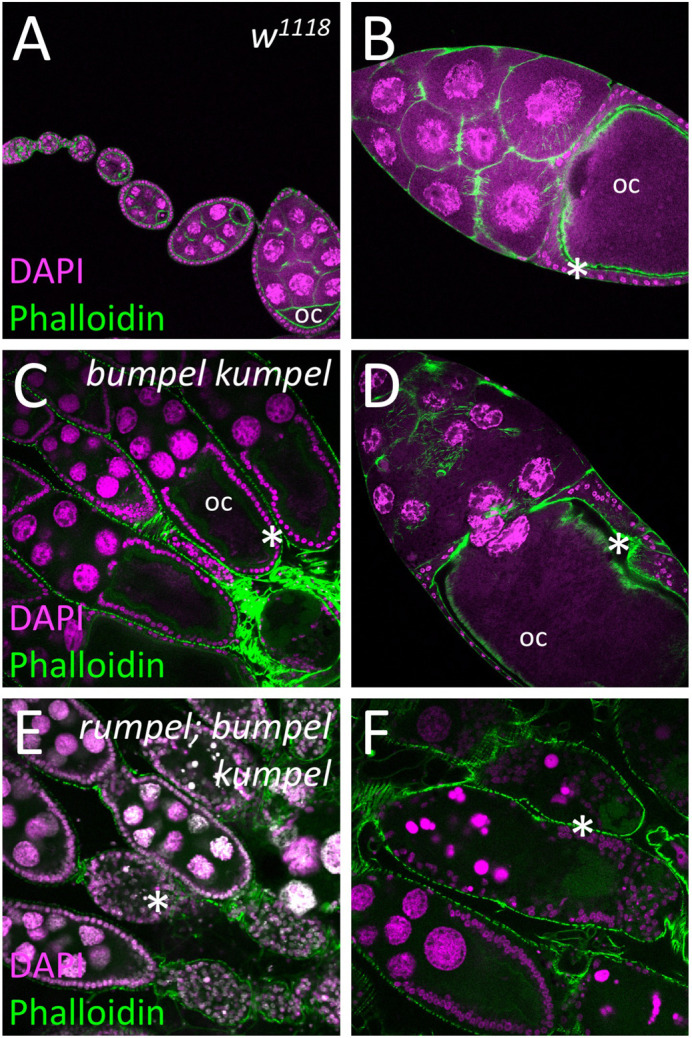
SLC5A transporters are required for the oogenesis. Confocal analysis of wild-type and mutant ovaries. Nuclei are labeled by DAPI staining, F-actin is shown following phalloidin staining (green). (A,B) In control females oogenesis developing egg chambers connected by stalk cells mature to form tubular ovarioles. During the previtellogenic phase, the future oocyte (oc) is defined which is positioned at the posterior pole. During the vitellogenic phases the oocyte grows exponentially and is surrounded by a cuboidal follicular epithelium (asterisks). (C,D) Homozygous bumpel kumpel double mutants are sterile but lay few eggs. Oogenesis is affected at the vitellogenic phase. The oocyte and the follicle epithelium degenerate. (E,F) Homozygous rumpel bumpel kumpel mutants are sterile and never lay eggs. Oogenesis is affected at the vitellogenic stage as seen in rumpel bumpel double mutants. However, the disintegration of oocytes and the follicular epithelium is more pronounced.
