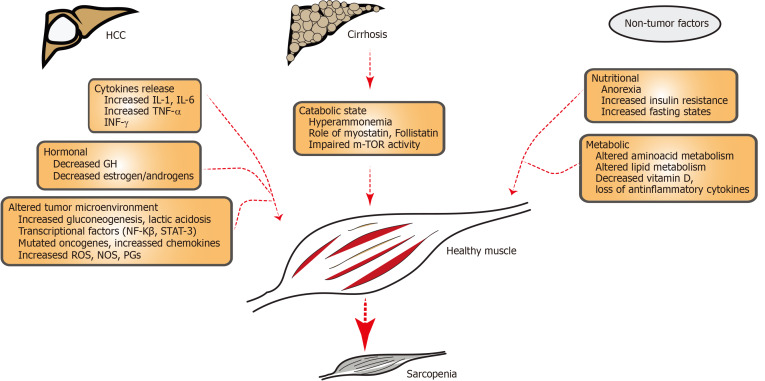
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration showing factors contributing to sarcopenia in hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis. Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma have increased release of cytokines, hormonal substances (GH, anabolic steroids) and altered tumor microenvironment (with hypercatabolic state, mutagenesis included by altered DNA, increased reactive oxygen species. Patients with HCC have underlying cirrhosis with hyperammonemia, decreased m-TOR activity which can contribute to sarcopenia. Non-tumor factors include poor nutrition and altered amino acid or lipid metabolism. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; IL-1: Interleukin-1; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alfa; INF-γ: Interferon gamma; GH: Growth hormone; NF: Nuclear factor kappa B; STAT-3; Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; NOS: Nitric oxide species; PGs: Prostaglandins; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin.