Fig. 1.
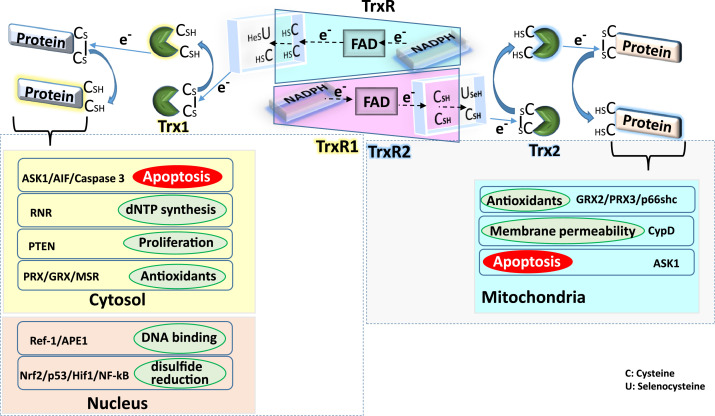
General functions of the thioredoxin system in cellular compartments
Trx1 reduces the disulfide bond in the proteins present in cytosol and nucleus and gets oxidized in the process. Active site Cys/SeC residues of TrxR1 reduce the oxidized Trx1 protein by transferring electron from NADPH through FAD. In cytosol, Trx1 is involved in the disulfide reduction of proteins involved in antioxidant defense (PRX/GRX/MSR), proliferation (PTEN), dNTP synthesis (RNR) and apoptosis (ASK1/AIF/Caspase 3). Whereas in the nucleus, Trx1 reduces disulfide bonds in transcription factors (NF-κB, Nrf-2, Hif1α, p53) and proteins regulating DNA binding (Ref-1, APE1).
In mitochondria, Trx2 reduces disulfide bonds in the proteins regulating mitochondrial redox (p66shc, GRX2 and PRX3), membrane permeability (CypD) and apoptosis (ASK1).