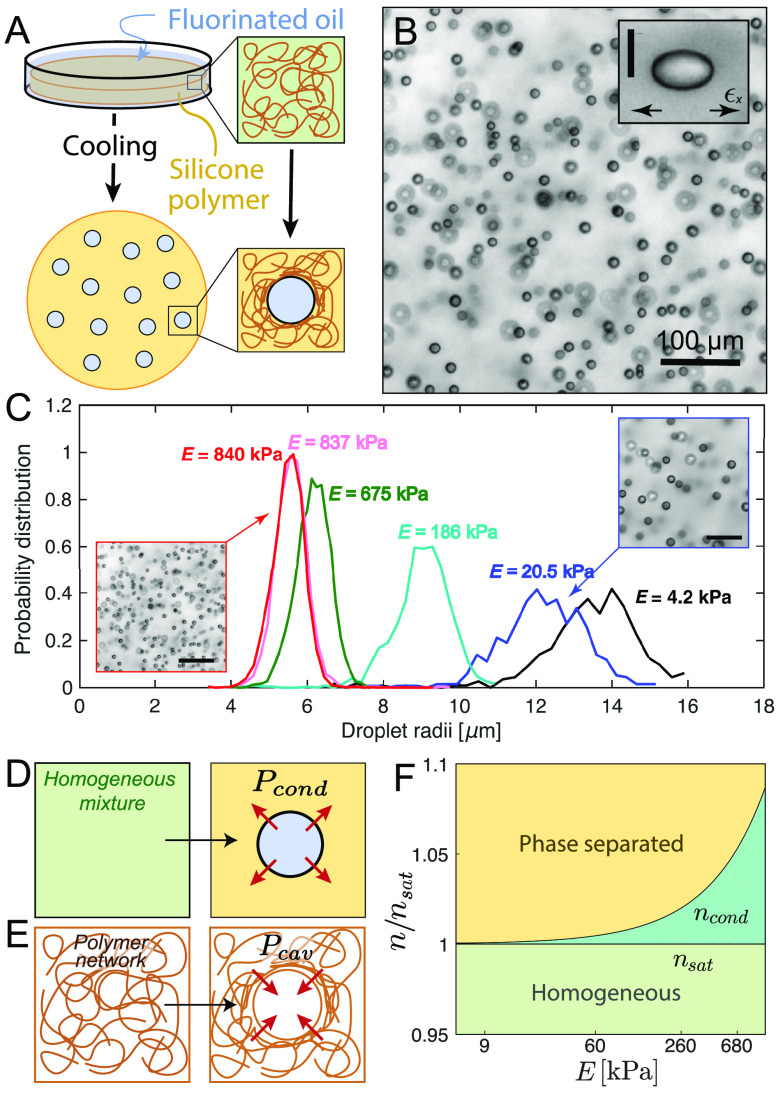
Figure 3.
Elastic control of phase separation. (A) Schematic diagram of temperature-induced nucleation and growth of fluorinated oil droplets in silicone polymer networks. (B) Bright-field microscopy image of the typical oil droplets formed in the silicone gels.52 Inset shows how network stresses cause the droplets to grow with elliptical shapes.55 The scale bar is 10 μm. (C) Typical droplet distributions in different gel stiffnesses, E. Microscopy images shown the evolution of the droplets’ number density with E.52 Scale bars are 80 μm. (D) Schematic of the condensation of a single droplet, exerting a condensation pressure, Pcond into the continuous phase. (E) Schematic of the creation of a spherical cavity on a polymer matrix. The opposing pressure exerted by the network is the cavitation pressure Pcav. (F) Phase diagram of the stability of an homogeneous mixture depending on the supersaturation of the mixture and the stiffness of the network.54 Reproduced with permission from ref (52), Copyright 2018 American Physical Society, from ref (54), Copyright 2020 Nature Research, and from ref (55), Copyright 2020 American Association for the Advancement of Science.