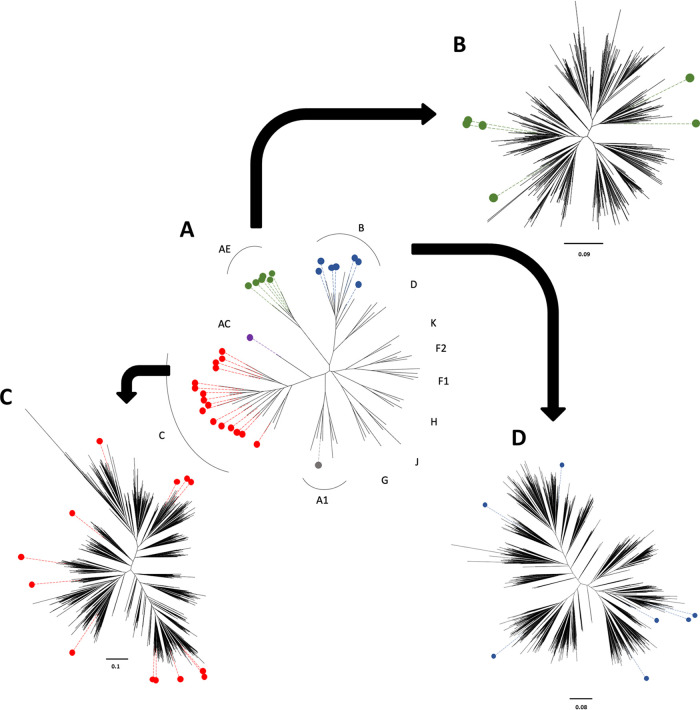
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic trees showing the genetic diversity covered by 29 Env-infectious molecular clones (IMCs). (A) env ectodomains from the 29 Env-IMCs we had available were aligned with sequences representing each major subtype (four sequences per subtype), and a maximum-likelihood tree was constructed. Six CRF01 A/E sequences (green) were then aligned with 549 superfiltered subtype A/E env sequences (B), 16 subtype C sequences (red) were aligned with 1,315 superfiltered subtype C env sequences (C), and seven subtype B sequences (blue) were aligned with 1,939 superfiltered subtype B env sequences (D) available in the Los Alamos database, and maximum-likelihood trees were constructed to show the genetic diversity covered by the three panels.