Figure 1.
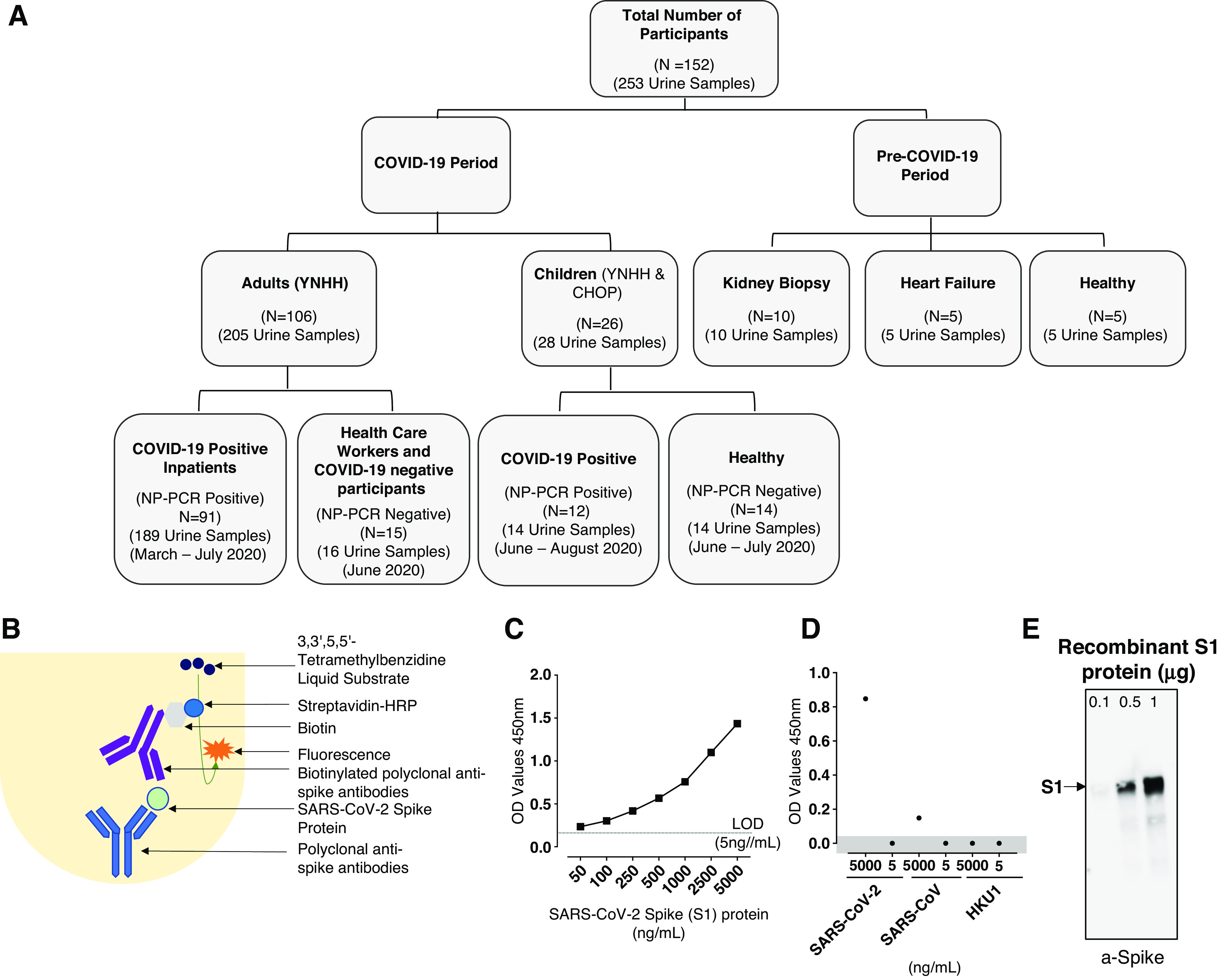
Consolidated summary of study population, assay chemistry, and sensitivity and specificity of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein using capture ELISA. (A) Flowchart describing the study population. Samples used in this study were collected both before and during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. (B) Schematic representation of the capture ELISA assay chemistry. (C) Representative standard curve generated using 5 µg/ml SARS-CoV-2 polyclonal anti-spike antibodies. LOD, limit of detection (D) Assay used to define the specificity of the SARS-CoV-2 capture ELISA. Two different concentrations (5 µg/ml and 5 ng/ml) of different human-infecting coronaviruses (SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and human coronavirus HKU1 [HCoV-HKU1]) were assessed to determine the specificity of the polyclonal anti-spike SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Data points in the shaded area are below the limit of detection. (E) Sensitivity of the polyclonal antibodies to detect SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 protein using Western blot. SARS-CoV-2 in three different concentrations was measured: 0.1 µg, 0.5 µg, and 1 µg. CHOP, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; NP-PCR, PCR of nasopharyngeal swab; YNHH, Yale New Haven Hospital.
