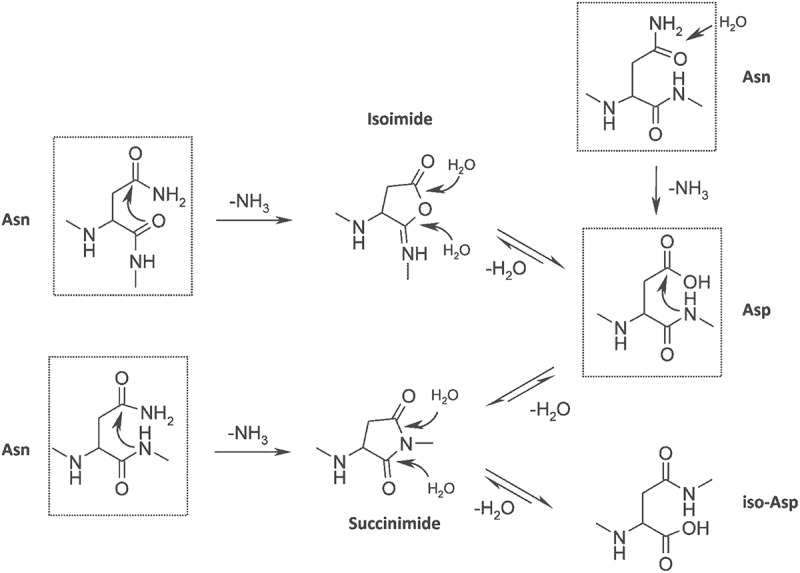
Figure 1.
Asparagine deamidation and aspartic acid isomerisation pathway. Reproduced from Sydow JF et al. (2014).46 (Creative Commons Attribution License).
Alt Text: The top half of the figure shows the removal of amine group from asparagine to form isoimide. Isoimide is hydrolysed by two water molecules hydrolysing isoimide to form aspartic acid in a reversible reaction. The top right-hand side of the figure shows the loss of an amine group from asparagine to form aspartic acid. The bottom half of the figure shows the loss of an amine group from asparagine to succinimide. The succinimide is hydrolysed by two water molecules to form aspartic acid and isoaspartic acid.