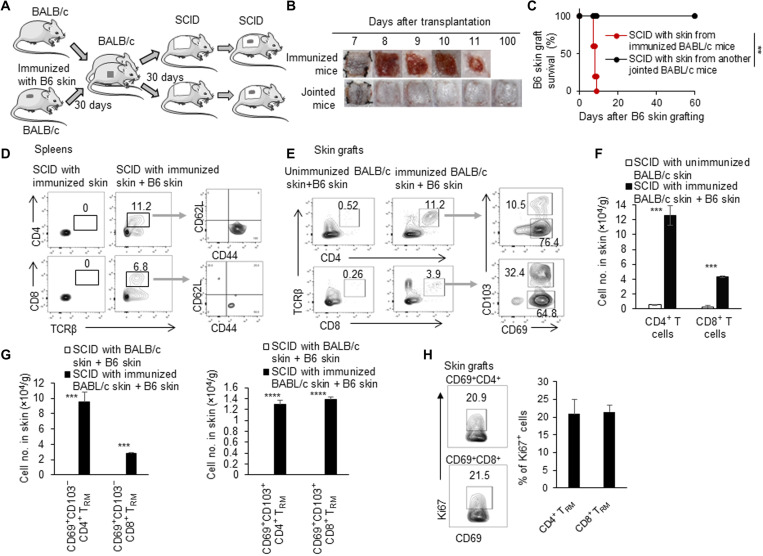
Fig. 3. Induced TRM cells in skin proliferated and mediated skin allograft rejection.
(A) Animal model: (i) We connected a previously immunized BALB/c mouse and an unimmunized BALB/c mouse. (ii) Thirty days later, the skin (2 cm by 2 cm) tissues from both immunized mice and jointed mice were transplanted onto two other SCID mice, respectively. (iii) C57BL/6 tail skin was then grafted onto these SCID mice. (B) Photos of C57BL/6 skin grafts. (C) C57BL/6 skin graft survival in SCID recipients with the unimmunized and immunized BALB/c skin tissue (n = 9 to 10 per group). (D) Flow cytometric analysis of CD4+, CD8+, CD62L+, and CD44+ T cells in spleens in SCID mice that received immunized BALB/c skin with or without C57BL/6 skin. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of CD4+, CD8+, CD103−CD69+, and CD103+CD69+ T cells in C57BL/6 skin grafts in SCID mice that received unimmunized and immunized BALB/c skin. (F) Quantification of numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in C57BL/6 skin grafts in SCID mice that received unimmunized and immunized BALB/c skin. (G) Quantification of numbers of CD103−CD69+ and CD103+CD69+ T cells in C57BL/6 skin grafts in SCID mice that received unimmunized and immunized BALB/c skin. (H) Flow cytometric analysis of Ki67 in CD4+CD69+ and CD8+CD69+ T cells in C57BL/6 skin grafts in SCID mice that received immunized BALB/c skin. Data are representative of independent experiments (n ≥ 3). Data are means ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, compared between the indicated groups.