Figure 4. Evolution of promoters.
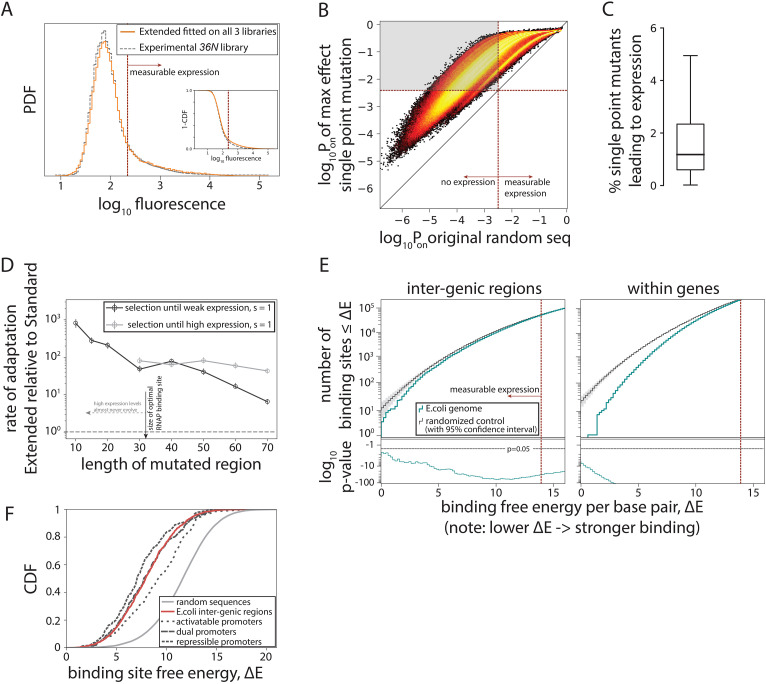
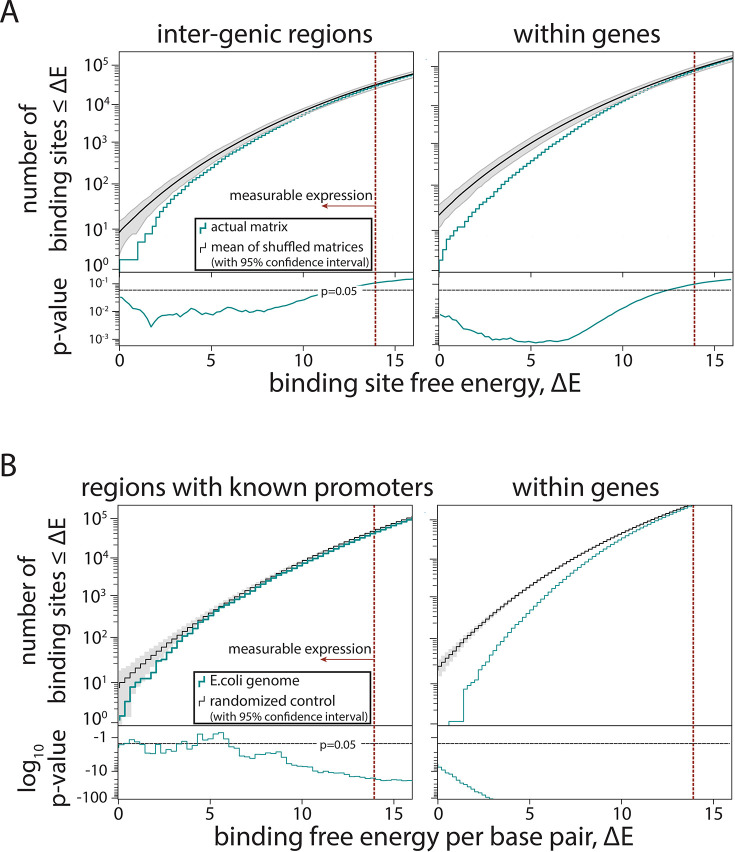
(A) Probability density function (PDF) for the flow cytometry measurement of the 36N library (gray dashed line) compared to the flow cytometry fluorescence intensities simulated from 106 randomly generated 115-bp-long sequences using the Extended model fitted on all three libraries. Red dotted line marks the cutoff for ‘measurable expression’, estimated from experimental data. Measurable expression is defined to correspond to the 99th percentile of fluorescence measurements of the experimental strain carrying no plasmid and, hence, no fluorescence. Inset: cumulative distribution function (CDF) for the same comparison. (B) Density heat map (brighter color represents higher density), showing, for every simulated random sequence (expression on x-axis), the expression of a single point mutant with the largest positive effect on predicted expression (Pon) (y-axis). For 82% of non-expressing random sequences (sequences left from the dotted line on the x-axis), that mutation led to measurable expression (gray area). (C) Box plot showing the percentage of all possible point mutations predicted to convert a given random non-expressing sequence into one with measurable expression (obtained from 105 random sequences). (D) Increase in rates of adaptive evolution of the Extended relative to the Standard model. Evolution to either weakest measurable expression, or high (PR) expression levels was modeled through single point mutations. Evolution was simulated 100 independent times for each of the 100 random 115-bp-long starting sequences, by mutating the central contiguous part of the indicated length. Evolving promoters would almost never reach high expression levels when only a region smaller than the RNA polymerase (RNAP) binding site (30 bp) was allowed to mutate. (E) For evidence of selection against σ70-RNAP binding sites, we compared the free energy per bp between either the inter-genic (typically, promoter containing) or the within-genic regions of the Escherichia coli genome, and that of a random sequence with the GC% of the corresponding region (note that higher energy means weaker binding and hence lower expression). At lower binding energies (corresponding to stronger binding), the actual number of binding sites in the E. coli genome (teal) is lower than expected based on random sequences (gray). Associated p-values are also shown. The total number of binding sites increases with binding energy (i.e. there are a lot more weaker than stronger binding sites), explaining the variability in p-values. (F) CDFs for predicted binding strengths of different E. coli promoters, obtained from RegulonDB. Figure 4—figure supplement 1 shows further details on how promoter evolution was modeled. Figure 4—figure supplement 2 contains the information about the contribution of cumulative binding to expression. Figure 4—figure supplement 3 shows additional tests for selection against σ70-RNAP binding sites.
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Modeling evolution.
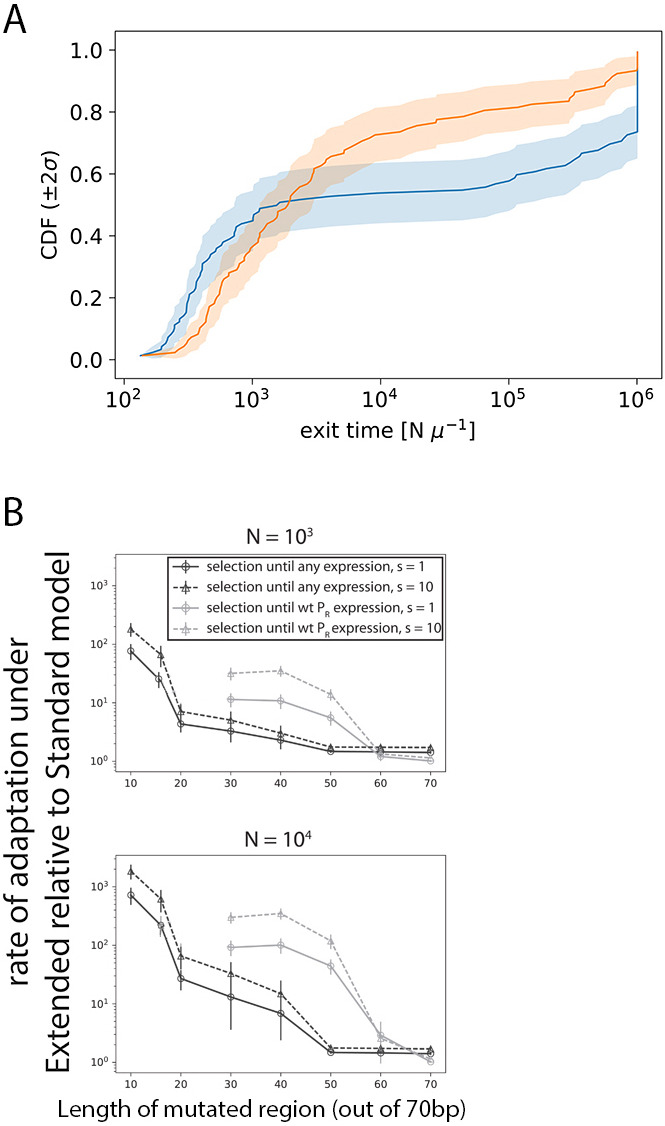
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Cumulative binding contributes more to expression at weak promoters.