Fig. 1 |. Activation of CAFs.
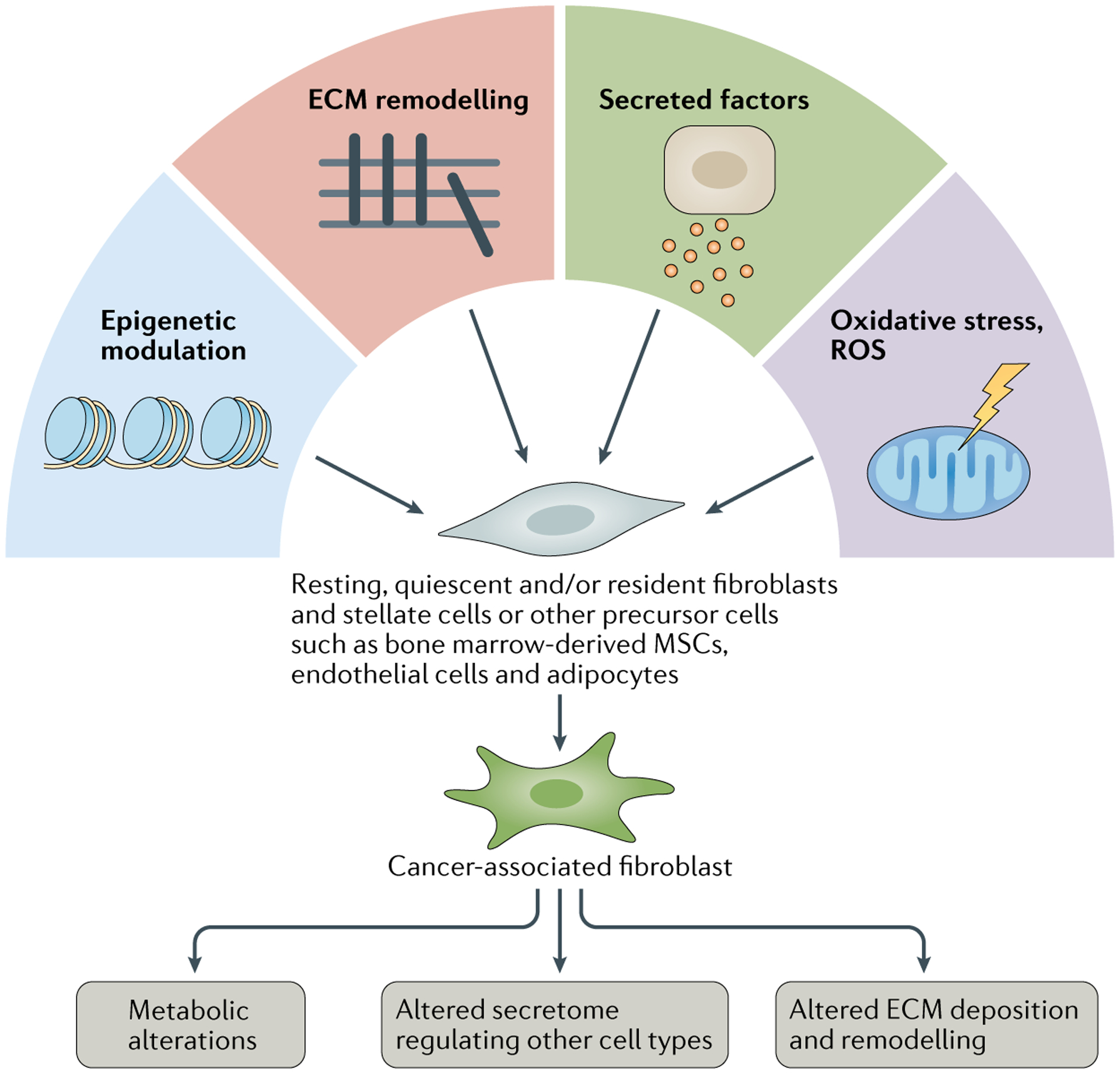
Schematic illustration of various mechanisms involved in cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) activation. Potential cellular origins of CAFs include quiescent, resting or specific tissue-resident fibroblasts (stellate cells), bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), endothelial cells and other cell types. ECM, extracellular matrix; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
