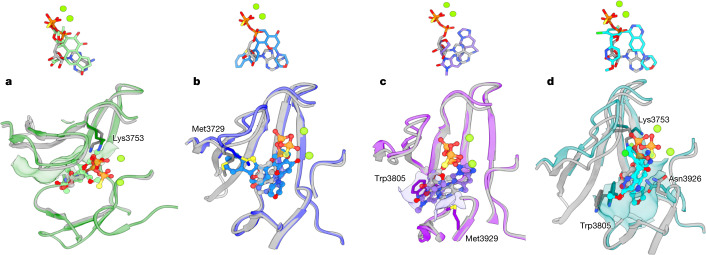
Fig. 3. Comparisons of the binding modes among ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and the four inhibitors.
a, Comparison of the binding modes of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and wortmannin in DNA-PKcs. Top, binding conformations of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 (light grey, ATPγS; fluorescent green, Mg2+ ions) and wortmannin (green). Bottom, conformational differences in the binding groove of DNA-PKcs between ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 (grey) and wortmannin (green). b, Comparison of the binding modes of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and NU7441 in DNA-PKcs. Top, binding conformations of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and NU7441 (blue). Bottom, conformational differences in the binding groove of DNA-PKcs between ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and NU7441 (blue). c, Comparison of the binding modes of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and AZD7648 in DNA-PKcs. Top, binding conformations of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and AZD7648 (purple). Bottom, conformational differences at the binding groove of DNA-PKcs between ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and AZD7648 (purple). d, Comparison of the binding modes of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and M3814 in DNA-PKcs. Top, binding conformations of ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and M3814 (cyan). Bottom, conformational differences at the binding groove of DNA-PKcs between ATPγS–(Mg2+)2 and M3814 (cyan).