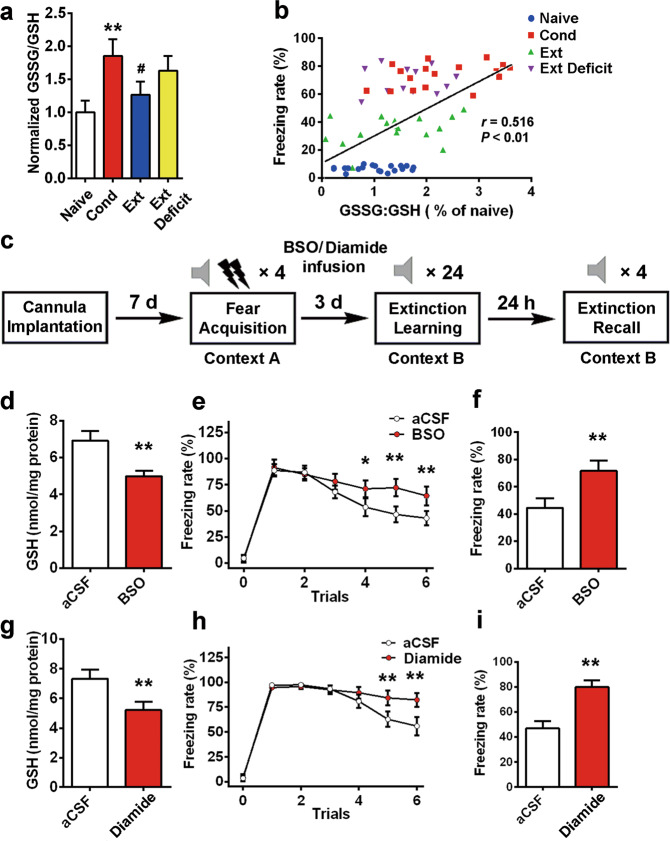
Fig. 3. Imbalance of redox homeostasis in the BLA by disrupted GSH function impairs extinction.
a The normalized ratio of GSSG/GSH is illustrated by the column graph (n = 10, **P < 0.01 vs. the naïve group, #P < 0.05 vs. the Cond group). b The association between the freezing rate and the GSSG/GSH ratio was assayed by Pearson correlation test (r = 0.516, P < 0.01). c The experimental protocols of BSO (1 mM, 0.5 μL) or diamide (300 μM, 0.5 μL) intra-BLA infusion. Rats received an infusion once per day (the first time was 24 h after training, and the last time was half an hour before extinction). d The GSH assay was performed 30 min after extinction recall (n = 12, **P < 0.01 vs. the aCSF group). e, f Rats received fear extinction in context B at 24 h after the last intra-BLA infusion of BSO or aCSF (n = 12, F(5,18) = 21.547, P < 0.01 for time × group interaction, post hoc LSD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). The freezing rate on extinction recall days was measured (n = 12, **P < 0.01 vs. aCSF group). g The GSH assay was performed at 30 min after extinction recall (n = 12, **P < 0.01 vs. the aCSF group). h Rats received fear extinction in context B at 24 h after the last intra-BLA infusion of diamide or aCSF (n = 12, F(5,18) = 27.382, P < 0.01 for time × group interaction, post hoc LSD, **P < 0.01). i Fear memory was assessed at 24 h after the extinction session by placing the animals in context B and measuring conditional freezing during tone presentation (n = 12, **P < 0.01 vs. aCSF group). All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a post hoc LSD test.