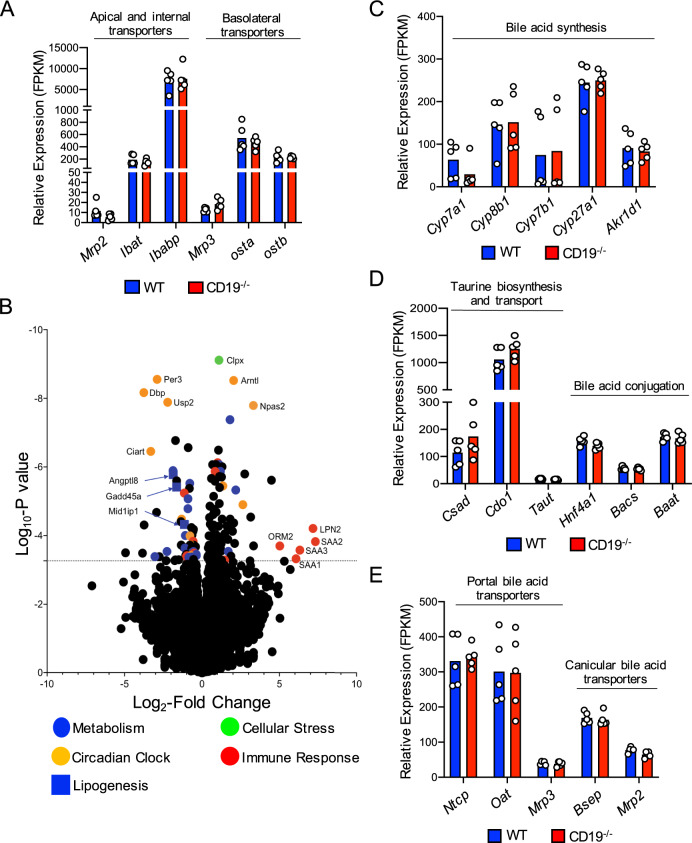
Fig. 2. BA abnormalities are not due to host defects in Bile acid synthesis, conjugation, or reabsorption in CD19−/− mice.
A Gene expression of bile acid transporters in the distal ileum of mice. B Volcano plot of major differentially regulated genes in the liver of CD19−/− mice compared to WT controls. The FDR-adjusted significance cutoff (FDR < 0.05) of quasi-likelihood hypothesis testing is illustrated by line along Y-axis. C Gene expression of liver enzymes involved in bile acid synthesis. D Gene expression of liver enzymes associated with taurine biosynthesis and bile acid conjugation. E Gene expression of liver bile acid transporters. A–E Data is representative of one ileal RNAseq and one liver RNAseq experiment each containing five biological replicates for each genotype. Significance determined by quasi-likelihood testing with an FDR significance cutoff of <0.05. None of the genes shown are differentially regulated based on FDR-adjusted p-values. Ileal and liver RNAseq data sets are derived from the same set of 5 female WT and 5 female CD19−/− mice. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.