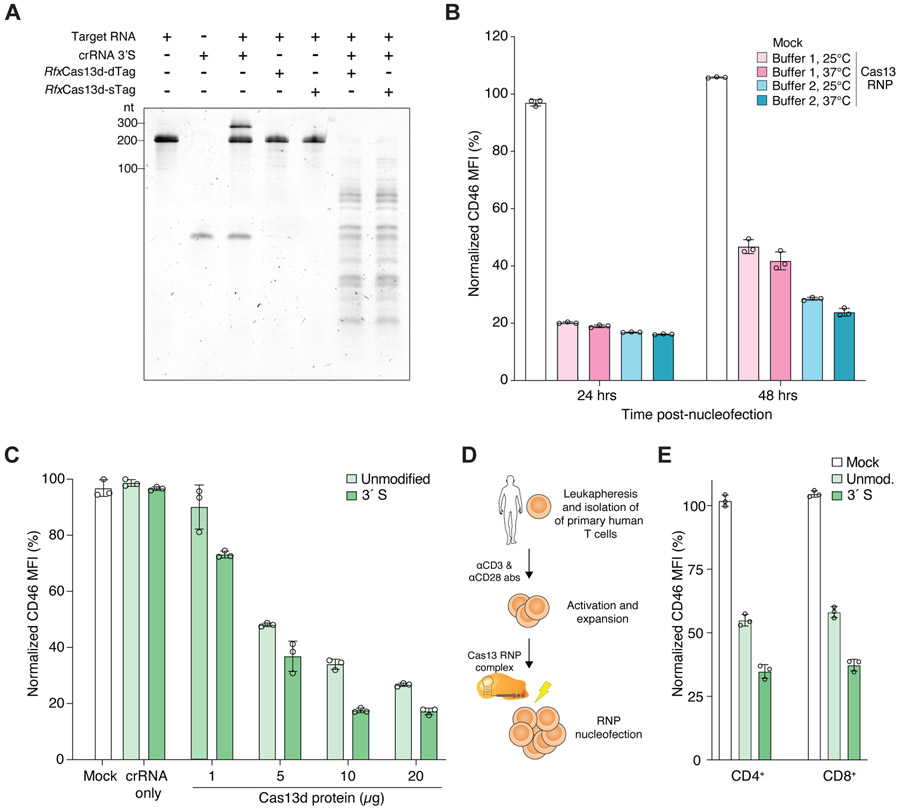
Figure 3. Robust knockdown in human cell lines and primary immune cells using Cas13d ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes and chemically-modified crRNAs.
(A) Denaturing TBE-urea gel showing the cleavage activity of the indicated RfxCas13d proteins tagged with either one (sTag) or two (dTag) affinity purification tags and their cleavage activity using a chemically-modified crRNA (3’S) targeting CD46. RfxCas13d-sTag includes only a C-terminal HA tag. RfxCas13d-dTag includes C-terminal HA and 6xHis tags and an N-terminal MKIEE solubility sequence. (B) CD46 expression in HEK293FT cells at 24 and 48 hours after nucleofection with Cas13 RNP complexed with Buffer 1 (GenScript) and Buffer 2 buffer (RNA cleavage buffer, see Methods) at the indicated temperature prior to nucleofection. (C) CD46 expression in HEK293FT cells at 24 hours after nucleofection with synthetic crRNAs only and Cas13 RNP complexes with different protein amounts (1, 5, 10 and 20 μg) complexed with CD46-targeting synthetic crRNAs with no chemical modification or with a phosphorothioate bond at the 3′ end (3′S). (D) Leukapheresis and activation of primary human T cells prior to Cas13 RNP electroporation. (E) CD46 expression in primary human T cells (CD4+ and CD8+) at 24 hours after nucleofection with Cas13 RNPs complexed with CD46-targeting synthetic crRNAs with no chemical modification or with a 3′S modification. Bars represent mean values ± s.d., n =3 biological replicate nucleofections.