Figure 3.
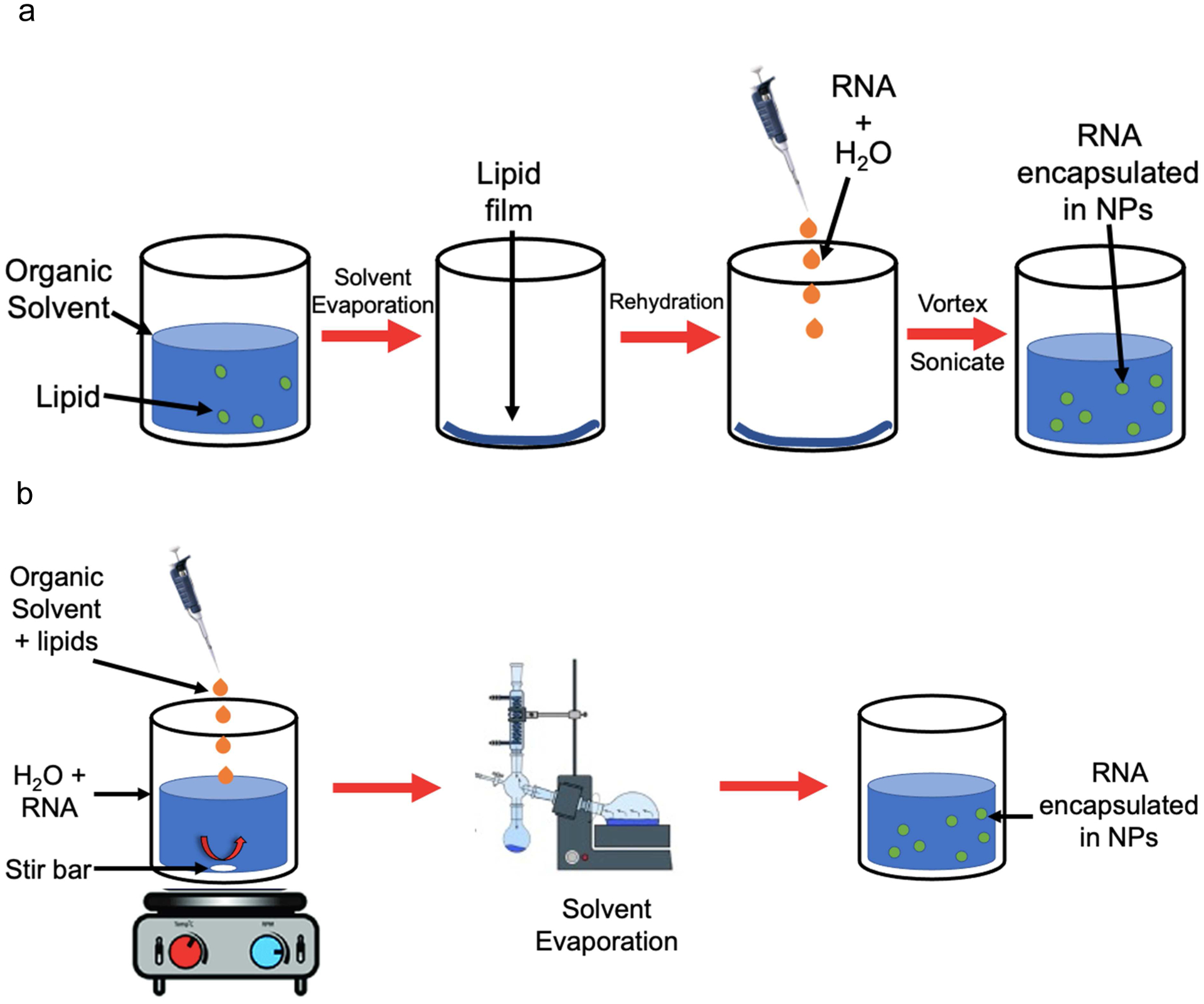
Schemes showing common methods of RNA encapsulation in lipid- and/or polymer-based NPs. a) Thin lipid film hydration. Lipids are suspended in an organic solvent, which is then evaporated under nitrogen flow. Further evaporation can be carried out under vacuum to ensure solvent evaporation. The resulting lipid film is rehydrated with an aqueous solution containing RNA, and then vortexed and sonicated to produce NPs containing RNA in their core. b) Nanoprecipitation. An organic solvent containing NP components (lipids and/or polymers) is added dropwise to an aqueous solution containing RNA while stirring. The solvent is evaporated under nitrogen or by using a Rotavapor, leaving an aqueous solution with NPs containing RNA in their core.
