Figure 1.
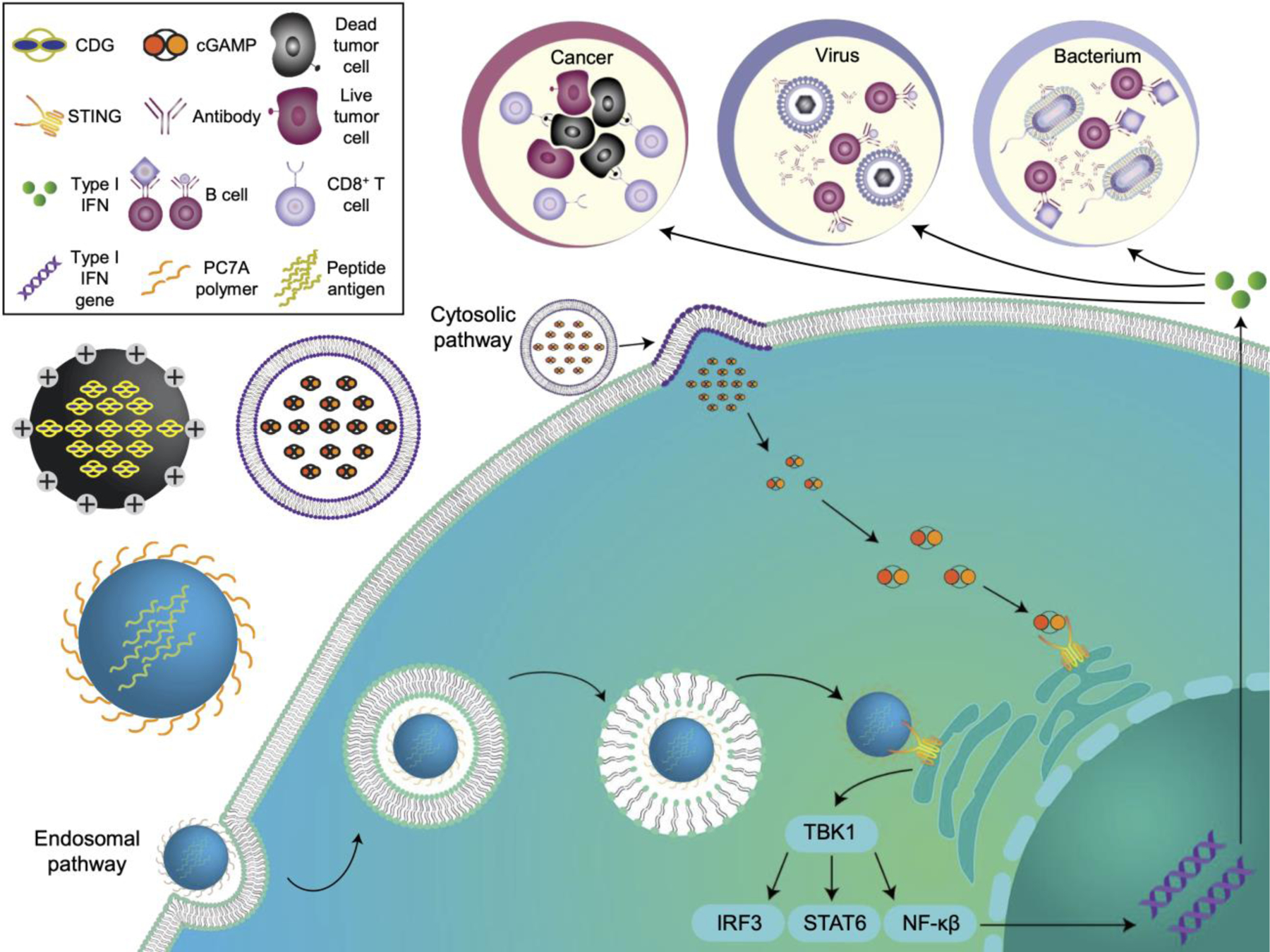
STING-activating nanovaccines against cancer, virus and bacterium. STING nanovaccines can be synthesized from various nanomaterials to deliver payloads intracellularly. After endocytosis, pH-responsive nanovaccines can escape from the endosome and engage with STING in the cytosol. In the cytosolic pathway, the nanovaccines can fuse directly with the plasma membrane to release the encapsulated payload into the cytosol. Once activated, STING complexes with TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and phosphorylates interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6), or nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) to stimulate the production of type I interferons (IFNs).
